Candidiasis: Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
Last updated: Feb 20, 2026
| Test Options |
|
| Treatment | Topical, oral, or intravaginal antifungal medication |
| Price |
|
| Appointment Options |
Same-day appointment (subject to availability). Book via WhatsApp: 88770326 or email: camden@atamed.sg |
| Clinic Locations |
Orchard: 1 Orchard Blvd
#05-09 Camden Medical Centre, S248649 Tanjong Pagar: 72 Anson Rd #01-02 Anson House, S079911 Jurong: 21 Jurong Gateway Rd, #02-08 CPF Jurong Building, S608546 |
What Is Candidiasis?
Candidiasis is a fungal infection caused by Candida species, most
commonly Candida albicans, which naturally
lives on the skin, mouth, gut, and genital areas but can cause infections when the body's
balance is disrupted. This condition is also historically known as monilia or moniliasis, a
term that may still be used in some clinical or community settings.
In healthy individuals, Candida exists in small amounts and is kept in check by the
immune system and other microorganisms. However, certain factors such as antibiotic use,
high blood sugar, a weakened immune system, or hormonal changes can lead to an overgrowth,
resulting in candidiasis.
This condition can cause discomfort, irritation, and fatigue, interfering with eating, sleeping, daily hygiene, or sexual activity, depending on the area affected.
Types of Candidiasis and Their Symptoms
Candidiasis can present in different forms and severities, and affect the skin, mouth (oral thrush), genitals (vaginal or penile thrush), or bloodstream (invasive candidiasis).
| Type | Description | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Vaginal candidiasis | Common in women and caused by overgrowth of Candida in the genital tract. |
|
| Oral candidiasis (thrush) | Affects the mouth and throat, often seen in infants, older adults, or individuals using antibiotics or inhaled steroids. |
|
| Cutaneous candidiasis | Affects the skin, especially in warm and moist areas such as the armpits, groin, and under skin folds. |
|
| Penile candidiasis | Less common and usually affects uncircumcised men or those with diabetes or poor hygiene. |
|
| Invasive candidiasis | A serious infection that spreads through the bloodstream and can affect internal organs, typically occurring in hospitalised or immunocompromised individuals. |
|
Causes of Candidiasis
Candidiasis occurs when the natural balance of microorganisms in the body is
disrupted, allowing Candida to multiply and cause infection.
Several common factors can contribute to this imbalance:
- Antibiotic use – Broad-spectrum antibiotics can reduce levels of beneficial bacteria that normally help keep Candida under control.
- Hormonal changes – Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, use of hormonal contraceptives, or hormone replacement therapy can affect the natural balance in the genital area, making it easier for Candida to grow.
- High blood sugar levels – Individuals with poorly controlled diabetes are at higher risk due to elevated glucose levels that support fungal growth.
- Moisture and hygiene factors – Wearing damp or tight clothing, or not drying skin folds properly, can create conditions favourable for fungal overgrowth.
- Weakened immune system – Although less common in the general population, conditions such as HIV, cancer treatments, or use of immunosuppressants can impair the body’s defences against infection.
- Sexual activity or transmission from a partner – Although candidiasis is not classified as a STI, it can occasionally be triggered or passed between partners.
How Is Candidiasis Diagnosed?
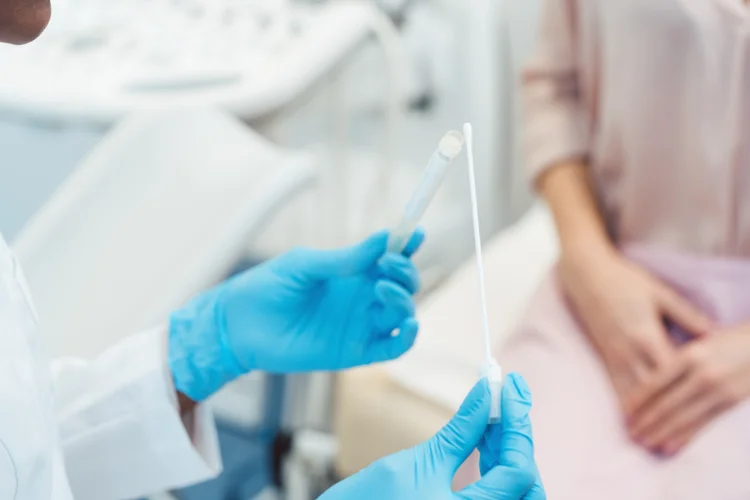
Candidiasis is usually diagnosed through physical examination and may be confirmed with laboratory tests depending on the location and severity of the infection.
- Swab and microscopy – A sample from the affected area is taken using a swab and examined under a microscope or cultured to detect the presence of Candida species.
- Blood tests – For suspected invasive candidiasis, blood cultures or specialised tests such as the β-D-glucan assay may be used to detect fungal components in the bloodstream.
- Pelvic examination – In women with vaginal symptoms, a pelvic examination along with a swab test can help confirm candidiasis and rule out other causes of similar symptoms.
Candidiasis Treatment
Treatment for candidiasis typically involves antifungal medications, with the approach depending on the type and severity of the infection.
- Topical antifungals – Creams, ointments or pessaries containing agents such as clotrimazole or miconazole are commonly used to treat skin and genital infections.
- Oral antifungals – Medications such as fluconazole may be prescribed for more widespread, persistent or recurrent cases.
In cases of invasive candidiasis, treatment requires intravenous antifungal therapy and is managed in hospital due to its potential to affect internal organs and cause serious complications.
Candidiasis Test & Treatment Cost in Singapore
At ATA Medical, we offer diagnosis and treatment for candidiasis, along with a range of other women’s health services.
| Test / Treatment | Test Type | Price* |
|---|---|---|
| Consultation | From $49.05 | |
| Testing | ||
|
DNA Probe/Multiplex Real Time PCR for Vaginitis Gardnerella vaginalis, Candida albicans and Trichomonas vaginalis |
Swab | $147.15 |
|
Basic Female Genital Screen (5 tests) Chlamydia PCR, Gonorrhoea PCR, Candida, Gardnerella Vaginosis, Trichomonas |
Swab | $268 |
|
Enhanced Female Genital Screen (9 tests) Chlamydia, Gonorrhoea, Mycoplasma genitalium, Mycoplasma hominis, Trichomonas, Ureaplasma parvum, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Candida, Gardnerella Vaginosis |
Swab | $348 |
|
Complete Female STD Screen (15 tests) HIV, Syphilis, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2, Chlamydia, Gonorrhoea, Mycoplasma genitalium, Mycoplasma hominis, Trichomonas, Ureaplasma parvum, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Candida, Gardnerella Vaginosisurealyticum, Candida, Gardnerella Vaginosis |
Blood + Swab | $478 |
| Treatment | ||
| Topical Antifungal Cream | From $10.90 | |
| Pessary Antifungal Cream | $59.95 for full course of treatment | |
| Oral Antifungal Medication | From $1.41 per tab | |
^Prices last updated on Jan 28, 2026. While every effort is made to keep pricing information up to date, please contact our team to confirm the latest rates.
We also offer discreet and confidential testing and treatment
for STIs, available as individual tests or in comprehensive packages. Male and female
doctors are available upon request to accommodate your comfort and preference.
Please contact
us directly for more information on test options, treatment availability, and appointment
scheduling.
How Can Candidiasis Be Prevented?
Preventing candidiasis involves maintaining a healthy balance of microorganisms in the body
and reducing factors that promote Candida overgrowth.
You can lower your risk by:
- Avoiding unnecessary use of antibiotics (speak with your doctor before stopping or starting any medication).
- Wearing breathable, moisture-wicking clothing.
- Practising good personal hygiene, especially in skin folds and genital areas.
- Managing blood sugar levels if you have diabetes.
- Avoiding douching or using scented hygiene products, which can disrupt the natural balance in the genital area.

Individuals who experience recurrent infections may benefit from lifestyle adjustments and regular medical check-ups to identify and manage any underlying health conditions.
When Should You See a Doctor for Candidiasis?
You should see a doctor if
symptoms are severe, persistent, recurrent, or if you are uncertain about the diagnosis.
Medical attention is especially important if:
- Symptoms do not improve after over-the-counter treatment.
- You experience frequent episodes of candidiasis.
- You have a weakened immune system or chronic condition.
- There are signs of systemic infection (e.g., fever, fatigue, unexplained illness).
Consult a Doctor for Candidiasis
ATA Medical @ Tanjong Pagar
Nearest MRT: Tanjong Pagar Station (EW15)
Contact Number: 6223 0682
Email: hi@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed
ATA Medical @ Orchard
Nearest MRT: Orchard Boulevard Station (TE13)
Contact Number: 6223 0682
Email: camden@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed
ATA Medical @ Jurong
Nearest MRT: Jurong East MRT Station (NS1/EW24)
Contact Number: 6348 6292
Email: jurong@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed


