When Should I Test for STDs?
Last updated: Feb 20, 2026
If you are sexually active, it is advisable to get tested for sexually transmitted diseases
(STDs). Factors that increase your risk include having multiple partners,
engaging in unprotected sex, or having a history of STDs.
Regular testing supports early detection and treatment, reducing the chances of
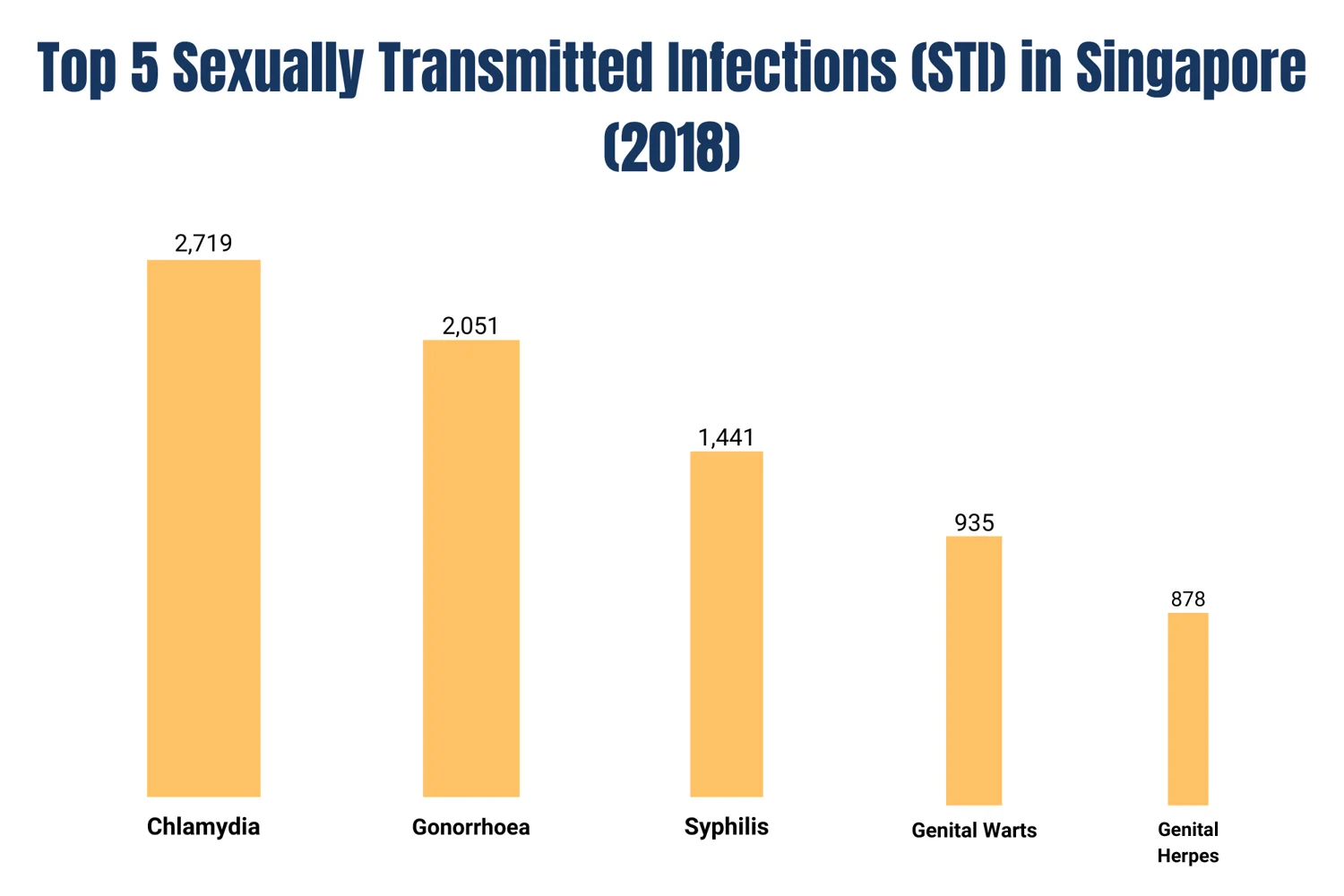
complications and transmission to others. Common STDs such as chlamydia
and gonorrhoea can often be
asymptomatic, making regular testing essential for maintaining your sexual
health.
High-Risk Sexual Behaviours

STD testing is generally recommended for:
- Everyone at least once
- People with new or multiple sexual partners
- People who engage in casual sex and/or unprotected sex
- People diagnosed with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
- Women aged 21 years and above, or below 25 years and are sexually active
- Pregnant women
In Singapore, this is especially important for young adults, given that those aged between 20-34 years had the highest rate of STIs in 2017 according to a Ministry of Health (MOH) report. Prompt testing is important for this age group to prevent the spread of infection and potential long-term health complications.
STD Window Periods and Potential Symptoms
STDs have varying window periods, which is the time after being exposed before a test can detect an infection in the body:
| Type of STD | Window Period for Testing |
|---|---|
| Chlamydia and Gonorrhoea | 24 hours to 6 days |
| Syphilis | 3 to 6 weeks |
| Herpes | 4 to 6 weeks |
| Hepatitis |
Hepatitis A: 2 to 7 weeks Hepatitis B: 6 weeks Hepatitis C: 8 to 9 weeks |
| Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) | 14 days |
Some common STDs symptoms can include:
- Unusual genital discharge
- Pain when urinating
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Loss of weight
- Sores
- Rash or itching
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
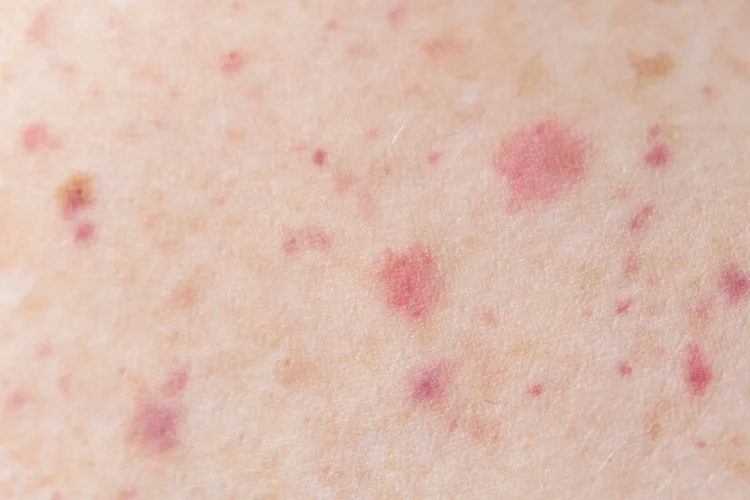
It is important to understand that these symptoms may be caused by other health conditions. However, if you experience these symptoms and are worried about a possible infection, please consult your doctor to obtain an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Asymptomatic Infections and Routine Testing
Many STDs, particularly chlamydia and gonorrhoea, often show no symptoms. If left untreated, this can lead to serious long-term health issues, such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women, which can cause infertility and chronic pain, and epididymitis in men, affecting sperm-carrying tubes. Regular STD testing is your best defence as it allows for early detection and treatment, preventing complications and reducing the risk of transmission. While annual testing is recommended for most sexually active individuals, those at higher risk such as having multiple partners or engaging in unprotected sex should consider more frequent testing.
Testing During Pregnancy
Pregnant women should test for STDs as part of their prenatal care. Untreated STDs can lead to complications such as transmission to the baby, miscarriage or stillbirth, preterm labour and delivery, low birth weight, or congenital anomalies. Timely testing and treatment during pregnancy are vital for both maternal and infant health.
Summary
Regular and prompt testing is crucial to ensuring optimal sexual health. By understanding your risk level and the window periods for STDs, you can make informed decisions about testing. Since most infections may be asymptomatic, regular testing is essential for early detection and treatment to prevent complications. Protect yourself and your partners by getting tested for STDs promptly if you are at risk or concerned about being infected.
Why Choose ATA Medical?







Delivering Care Patients Appreciate
What to Expect
FAST RESULTS
We strive to deliver your results within 7 working days.
MINIMUM WAITING TIME
Our patient-oriented processes ensure your waiting time is kept to a minimum.
Friendly Service
Service is a top priority for us at ATA Medical.
Email Us at camden@atamed.sg for more
information.
Book your STD screening with us at 88838892


