What Does a Full Health Screening Include?
Last updated: Feb 20, 2026
Health screenings help detect potential health issues before symptoms develop. While basic
screenings typically cover essential checks such as blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood glucose,
a full health screening goes further by assessing multiple aspects of your health, including
comprehensive blood tests, imaging, and physical examinations.
This provides a clearer picture of your overall condition and supports early detection of conditions
that may require attention.
At ATA Medical, we provide a range of health screening
packages tailored to different ages, lifestyles, and risk profiles. Not sure which one suits
you? Speak to our doctors for a personalised assessment and guidance.
Basic vs. Comprehensive Health Screenings: Understanding the Difference
Basic Health Screening
Basic Health Screening primarily focuses on fundamental health assessments. It typically includes a physical examination, biophysical measurements like height, weight, and blood pressure, and basic laboratory tests such as blood and urine analysis. This level of screening is designed to catch common conditions, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol, providing a general overview of an individual's health status.
Comprehensive Health Screening
Comprehensive Health Screening, on the other hand, goes much deeper. Beyond the basics, it includes
a wider array of tests and evaluations, such as advanced blood work, radiological imaging like
X-rays and ultrasounds, and specific screenings for cancers, heart disease, and more. It may also
incorporate lifestyle assessments and counselling to provide a holistic view of one's health. This
type of screening is particularly beneficial for those with higher risk factors due to family
history, age, pre-existing health conditions, or lifestyle choices.
Understanding the distinction between basic and comprehensive screenings helps individuals make
informed decisions about their health care, aligning their choice of screening with their
specific health concerns and goals.
Components of a Full Health Screening
Physical Examination
A physical examination conducted by a doctor is a fundamental part of any health screening. This hands-on check involves inspecting the skin, eyes, heart, lungs, and abdominal organs to identify any possible health concerns. Our general consultation services offer thorough physical assessments customized to your health needs.
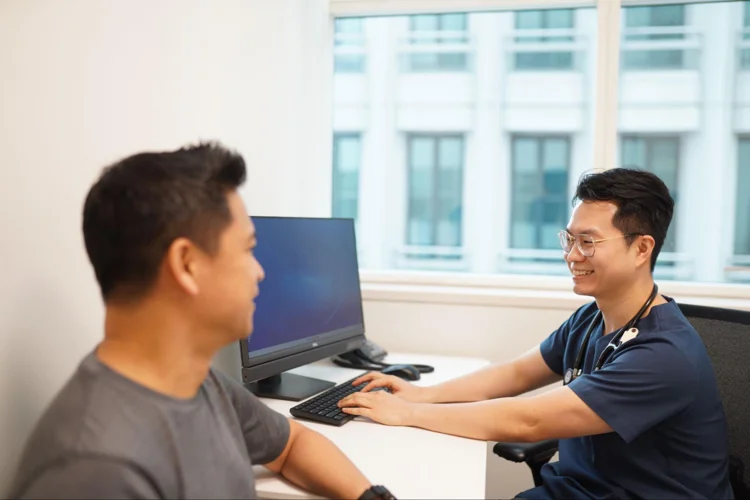

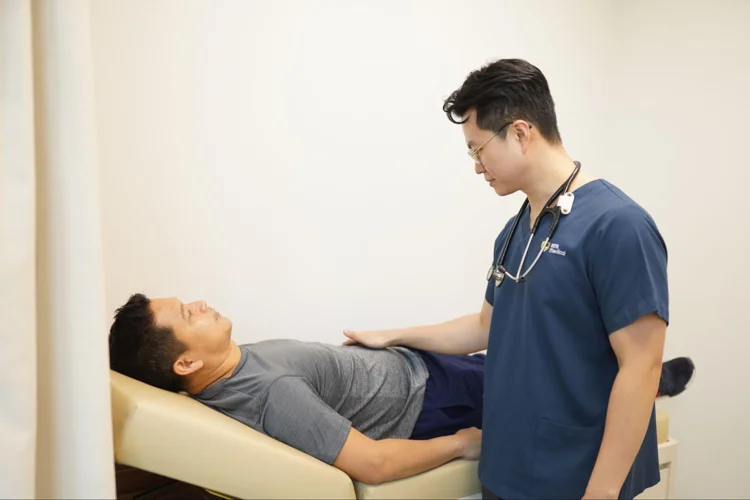


Biophysical Measurements
These measurements provide baseline data about your health:
- Height and Weight: Used to calculate Body Mass Index (BMI), a measure of body fat based on height and weight. This can be used to help with weight management.
- Visual Acuity and Colour Vision: Tests to assess the quality of your vision and detect potential issues. Our eye screening services can help identify vision problems early.
- Waist and Hip Ratio: A significant measure that helps assess the distribution of body fat. This ratio is calculated by dividing the circumference of your waist by that of your hips. It is an important indicator of health because it provides insight into potential risk factors for conditions such as cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. A higher ratio suggests a greater risk of heart disease and other health-related issues associated with abdominal obesity.
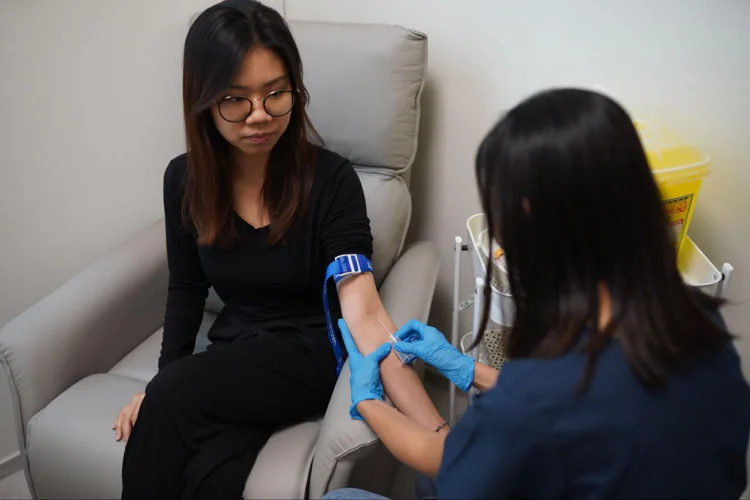
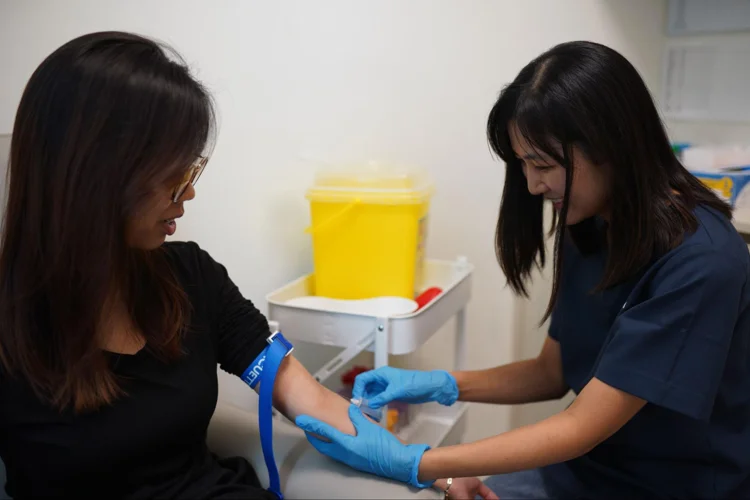
Laboratory Tests
A series of blood, urine, and sometimes stool tests that offer insight into various health markers:
- Blood Tests: Evaluate several components, including blood count, sugar levels (diabetes indicator), cholesterol levels, kidney function and liver function, thyroid hormone levels, cancer markers, sexually transmitted diseases, hepatitis A and B, and ABO blood group.
- Urine Tests: Screen for infections, sugar content (diabetes), protein (early kidney disease), and blood (indicative of infections, tumours, or kidney stones). Our urine tests provide detailed analysis of your urinary health.
- Stool Tests (Optional): Check for blood in the stool, a potential marker for colon cancer or other conditions like haemorrhoids.


Radiological Tests
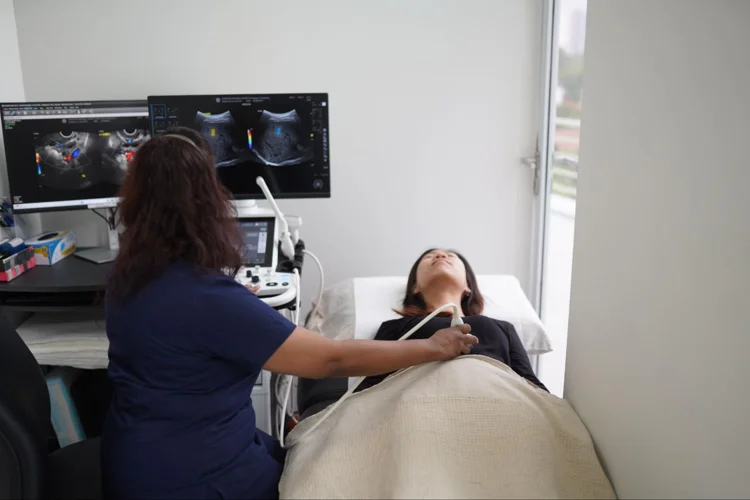
Radiological tests use imaging to look inside the body for signs of health conditions. These include:
- X-Ray: A quick and painless procedure often used to examine the lungs, bones, and other areas for abnormalities.
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of the inside of the body, such as the liver, gallbladder, kidneys, and, in women, the pelvic region and thyroid gland.
- Bone Mineral Density (BMD): A bone mass density test utilises X-rays to measure the density of bones, helping to diagnose osteoporosis or assess fracture risk. It can be recommended for women aged 65 and above or individuals with risk factors for osteoporosis.


Other Key Health Tests
In addition to radiological tests, a full health screening often includes the following key health tests:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): A quick and painless procedure used to assess the heart's electrical activity and detect potential cardiac abnormalities. For more comprehensive heart check ups, you may consider our treadmill stress test.
- Pap Smear / HPV Tests: PAP Smears and HPV Tests may be used for cervical cancer screening in women aged 25 – 65 who have been sexually active.
- Mammogram: An X-ray of the breasts recommended for breast cancer screening. Women aged 40 – 49 are advised to have it annually, while those 50 and above should have it every 2 years.
Advanced Screenings in Comprehensive Health Packages
Comprehensive health screenings often encompass a variety of tests for a deeper investigation into
one's health, including advanced screenings for cancer markers and detailed evaluations of
cardiovascular risks.
Among these, Computed Tomography
(CT) Scans, such as the CT
Calcium Score and CT Low Dose Lung Screening, play a crucial
role. The CT Calcium Score is used to assess the risk of coronary artery disease by measuring the
amount of calcified plaque in the coronary arteries.
Meanwhile, the CT Low Dose Lung Screening is designed to detect early signs of lung cancer,
especially in individuals at high risk
due to a history of heavy smoking or those with family history of lung cancer. These specialised CT
scans offer valuable insights, allowing for early intervention and management of potential health
issues.


Special Considerations for Health Screenings
Health screenings should be personalised based on age, gender, family history, existing health conditions, and lifestyle factors. These considerations help determine the most relevant screenings for each individual, ensuring that the focus is on the areas of greatest concern or risk.
Conclusion: Tailoring Your Full Health Screening
The essence of a full health screening lies in its ability to be tailored to the unique needs of
each individual. Consulting with a doctor is paramount in creating a personalised health screening
schedule that aligns with your health status, risks, and lifestyle. Regular health screenings are
instrumental in early disease detection and prevention, setting the foundation for a healthier
future.
Don't wait for symptoms to appear before taking action. Schedule a
consultation today to discuss
your health screening needs and take a proactive step towards maintaining your health. Remember,
early detection is key to preventing and successfully treating many health conditions.
Why Choose ATA Medical?


How Do I Book a Health Screening With ATA Medical?
ATA Medical @ Tanjong Pagar
Nearest MRT: Tanjong Pagar Station (EW15)
Contact Number: 6223 0682
Email: hi@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed
ATA Medical @ Orchard
Nearest MRT: Orchard Boulevard Station (TE13)
Contact Number: 6223 0682
Email: camden@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed
ATA Medical @ Jurong
Nearest MRT: Jurong East MRT Station (NS1/EW24)
Contact Number: 6348 6292
Email: jurong@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed





