Stroke Screening
Last updated: Jan 16, 2026
Stroke screening plays a crucial role in detecting risk factors or early signs of cardiovascular problems that could lead to a stroke. A stroke is a serious health event that happens when blood flow to the brain is disrupted, cutting off oxygen and nutrients. This disruption can cause lasting brain damage or even be fatal. Regular screening helps with early detection and timely treatment, giving individuals the opportunity to take preventive actions such as making lifestyle changes, taking medication, or undergoing surgery to lower their risk of stroke.

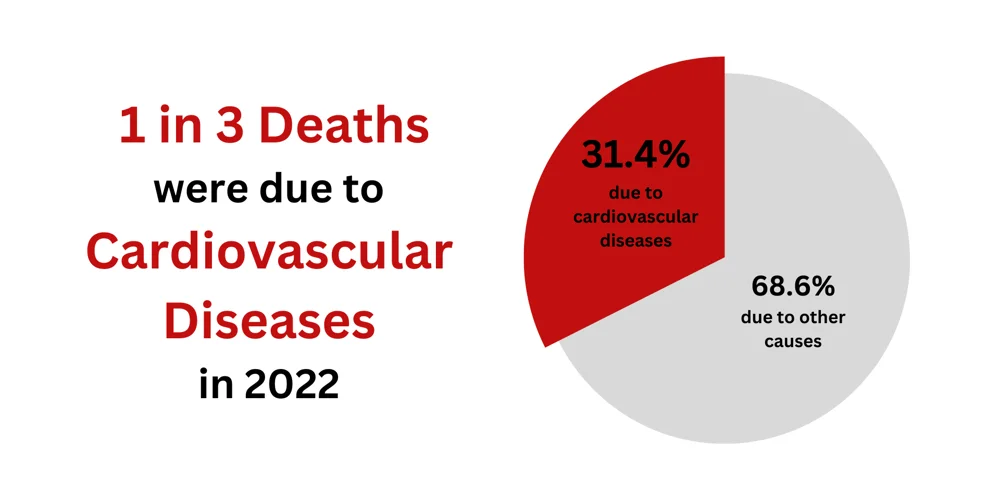
The World Stroke Organization estimates 1 in 4 persons will likely suffer from a stroke in their lifetime. Stroke is also one of the leading causes of death in Singapore, with cardiovascular diseases accounting for one-third of all deaths in 2022. Survivors often face significant health challenges, including long-term disability and a reduced quality of life. Therefore, early detection through regular screening is vital.
Types of Stroke
There are three primary types of stroke:
- Ischemic Stroke: The most common type, caused by a blood clot blocking an artery in the brain, reducing blood flow and oxygen. It can result from a thrombus (clot in the artery) or an embolus (clot from elsewhere in the body).
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: Less common but more severe, it occurs when a blood vessel in the brain bursts, causing bleeding, usually due to high blood pressure or aneurysms (weakened blood vessel walls).
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA): Also known as a "mini-stroke," a TIA is a temporary blockage of blood flow to the brain, with symptoms similar to a stroke but lasting only minutes to hours. TIAs are warning signs of a future stroke.
Common Risk Factors for Stroke
Several factors increase the risk of stroke such as:
- Chronic Conditions: Hypertension can damage blood vessels, while diabetes and high cholesterol contribute to the buildup of plaque in arteries (atherosclerosis). All of these conditions can lead to blockages or ruptures in blood vessels.
- Existing Heart Conditions: Atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat) can cause blood clots that may travel to the brain.
- Smoking: Smoking accelerates the development of atherosclerosis, increases blood clotting, increases blood pressure, and reduces blood oxygen levels.
- Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyle: Excess weight and lack of physical activity contribute to chronic conditions that are significant stroke risks.
- Age and Gender: Stroke risk increases with age, doubling every 10 years after the age of 55. While men have a higher overall risk of stroke, women tend to experience more severe outcomes.
- Family History: Family history of stroke or cardiovascular disease increases the risk due to shared genetic factors that predispose individuals to chronic conditions.

Types of Screenings for Stroke Risk
There are several types of screening tests that can indicate a risk of stroke such as:
| Tests | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Blood Tests | Diagnose chronic conditions like high cholesterol and diabetes. Blood tests can also monitor the effectiveness of medications aimed at reducing stroke risk. |
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | Detects irregular heart rhythms such as atrial fibrillation. |
| 2D Echocardiogram | Uses ultrasound to detect blood clots or structural abnormalities that could cause a stroke. |
| CT Coronary Angiogram | Produces detailed images of coronary arteries to detect blockages or narrowing in these vessels. |
| CT Calcium Score | Measures calcium deposits in coronary arteries, with higher scores indicating a greater risk of atherosclerosis and stroke. |
| Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) Ultrasound | Measures the thickness of the carotid arteries' inner layers to assess plaque buildup and atherosclerosis risk. |
| Brain CT Scan | Provides detailed brain images to detect haemorrhages, ischaemic stroke and aneurysms that increase stroke risk. |
| Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) | Offers detailed images of brain tissue and blood vessels, making it useful for identifying smaller or earlier strokes and assessing the extent of brain damage. |
Costs of Stroke Screening in Singapore
At ATA Medical, we offer a range of tests to screen for cardiovascular risks, including those related to stroke:
| Test | Price* |
|---|---|
| Consultation | From $49.05 |
| Apolipoprotein B | $32.70 |
| HsCRP | $38.15 |
| Lipoprotein (a) | $59.95 |
| Fasting Insulin | $66.49 |
| Homocysteine | $74.12 |
| Essential Lipid Profile: Full Cholesterol Test (Total, LDL, HDL, Triglycerides, HDL Ratio) | $21.80 |
| Cardiac Screening 3: Essential Lipid Profile + Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) + HsCRP | $63.22 |
|
Cardiac Screening 4: Cardiac Screening 3 + Homocysteine + Fasting Insulin +
Glucose
Note: Fasting is required for accurate results of Fasting Insulin and Glucose |
$172.22 |
| Stroke Screen (includes MRA, COW & Carotids) | $1,231.70 |
| ECG** | $49.05 |
| 2D Echocardiogram | $436 |
| CT Coronary Angiogram | $1,384.30 |
| CT Calcium Score | $403.30 |
| Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) Ultrasound | $163.50 |
| Brain CT Scan | From $599.50 |
| Brain MRI Scan | From $1,122.70 |
^Prices last updated on Jan 28, 2026. While every effort is made to keep pricing information up to date, please contact our team to confirm the latest rates.
**2D Echocardiogram will be done at the cardiologist clinic and vetted by the cardiologist.
Alternatively, you may want to explore our health screening packages for a more thorough assessment of your health.
Where to Screen for Stroke Risk in Singapore
ATA Medical is conveniently located at two different locations:
- Tanjong Pagar Medical Clinic (Closest MRT: Tanjong Pagar EW15)
- Orchard Clinic (Closest MRT: Orchard Boulevard TE13)
Conclusion
Regular stroke screening allows for early detection of risk factors and signs that could lead to a stroke. By identifying these risks early, individuals can take preventive measures, such as lifestyle changes and medication, to reduce their risk. With 1 in 4 people likely to experience a stroke in their lifetime, incorporating stroke screening into your healthcare routine is a proactive step toward maintaining long-term health and preventing severe outcomes. If you are unsure which screenings are appropriate for you, consult a doctor to discuss the best approach.
How Do I Book a Stroke Screening Appointment?
ATA Medical @ Orchard
Nearest MRT: Orchard Boulevard Station (TE13)
Contact Number: 6223 0682
Email: camden@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed
ATA Medical @ Tanjong Pagar
Nearest MRT: Tanjong Pagar Station (EW15)
Contact Number: 6223 0682
Email: hi@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed


