STD Rash: What You Need to Know About This Symptom
Last updated: Oct 27, 2025
What Is an STD Rash?
A sexually transmitted disease (STD) rash is a change in the skin that
may indicate an infection spread
through sexual contact. These rashes can vary from small red bumps to
larger patches, blisters, or sores. Depending on the specific type of STD, the
rash may appear on different areas of the body, such as the genital region, hands, chest, or
even the palms and soles, and can be contagious.
Although STDs are often linked to symptoms like pain during urination or unusual discharges,
skin changes are sometimes overlooked. Recognizing which STDs can cause rashes, how they
look, and when to seek medical care is important for early detection and
treatment. If you notice any symptoms, early STD
testing can help safeguard your sexual
health.
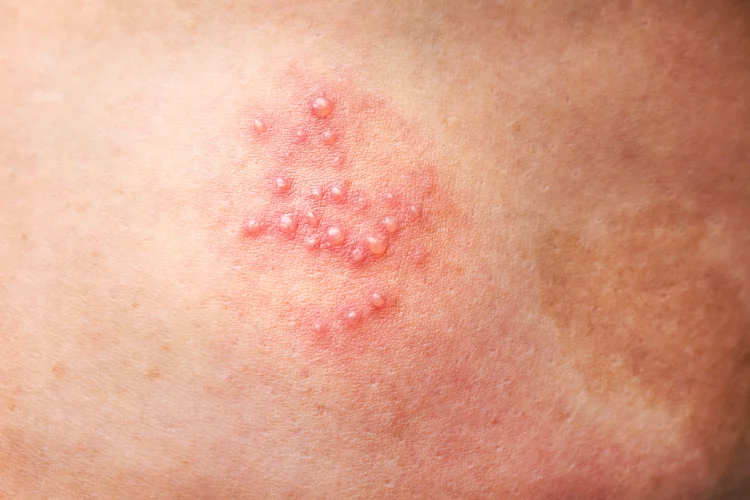
STDs That Can Cause Skin Rashes
Here is a brief breakdown of STDs that can cause rashes as a symptom:
| STD | Description | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
| Syphilis | A bacterial infection that progresses through distinct stages, with the secondary stage often marked by a rash. | Reddish-brown spots or patches, typically appearing on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. The rash is usually non-itchy and can spread across the body. |
| Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) | A viral infection caused by HSV-1 or HSV-2, known for causing sores or blisters in the oral or genital areas. The infection often manifests as rash-like outbreaks. | Painful, fluid-filled blisters that group together and crust over. Often found on the mouth, genitals, or surrounding skin. |
| Gonorrhoea - Disseminated Gonococcal Infection (DGI) | A bacterial infection primarily affecting mucous membranes, which in severe cases can spread and cause systemic symptoms, including rashes. | Red or purplish skin rashes that may appear as small pustules or raised lesions, often accompanied by spots on the trunk or limbs. |
| HIV | A viral infection that compromises the immune system, potentially leading to rashes during the acute phase or due to other infections in later stages. | Red, flat, or slightly raised rashes that can occur anywhere on the body. Often appears as a widespread rash with small bumps or blotchy skin. |
| Chlamydia | A common bacterial infection that, although primarily asymptomatic, can lead to complications such as reactive arthritis, which may present with a rash. | Rash associated with reactive arthritis often appears as small red spots or patches on the skin, particularly on the legs. |
| HPV | A viral infection with various strains, some of which cause genital warts that resemble a rash. These warts can spread and change appearance over time. | Flesh-coloured bumps or warts that may be smooth or cauliflower-like in texture, primarily located in the genital or anal region. |
Other Signs & Symptoms to Look Out for
If you develop a rash that you suspect to be related to an STD, it is important to consider any other accompanying symptoms, such as:
- Persistent or recurring rashes
- Rashes that develop after sexual activity
- Itching or burning sensations
- Fever or flu-like symptoms alongside the rash
- Swollen lymph nodes, particularly in the groin or neck
- Sores or ulcers on or around the genital area
- Unusual discharge from the genitals
- Pain during urination
Men experiencing rashes alongside genital symptoms such as discharge, itching, or inflammation should also consider conditions like penile infection, which can sometimes occur alongside or be mistaken for STD-related symptoms.
While these signs can indicate an STD, not all rashes and symptoms are related to STDs. Seeking medical evaluation is essential for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.

Diagnosis of STD Rashes
To accurately determine the cause of an STD-related rash, your healthcare provider may carry out:
- Physical Examination: A thorough inspection of the rash to assess its characteristics, such as size, colour, and location. This helps to form an initial assessment and determine which tests may be needed.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests, swabs, or biopsies of the affected area to confirm the specific type of infection. These tests can also check for any co-infections and may require some time for results to be processed.
Treatment of STD Rashes
The treatment of an STD-related rash focuses on symptom relief and addressing the underlying infection:
- Symptomatic Relief: Topical creams and pain relievers can be used to ease discomfort and reduce inflammation associated with rashes.
- Bacterial Infections (e.g., syphilis, gonorrhoea, chlamydia): Treated with antibiotics to eliminate the infection and prevent further complications.
- Viral Infections (e.g., herpes, HIV): Although there is generally no cure, these infections can be managed with antiviral medications to control symptoms, reduce the viral load, and prevent or reduce the frequency of outbreaks that may include symptomatic rashes.
Timely diagnosis and treatment can prevent the progression of STDs, reduce the risk of complications, and limit transmission to sexual partners. Prevention is always best and can be achieved by practising safe sex, regular STD screenings, and maintaining open communication with partners.
Summary
STD rashes are a significant yet often overlooked symptom of various sexually transmitted infections. Recognising the signs of an STD rash and associated symptoms and seeking medical attention is essential for early detection, as the only way to confirm if you have an STD is through testing. Prompt treatment helps reduce the risk of complications and protects your sexual partners. If you suspect you have an STD rash or other related symptoms, consult a doctor and get tested as soon as possible.
Why Choose ATA Medical?







Delivering Care Patients Appreciate
What to Expect
FAST RESULTS
We strive to deliver your results within 7 working days.
MINIMUM WAITING TIME
Our patient-oriented processes ensure your waiting time is kept to a minimum.
Friendly Service
Service is a top priority for us at ATA Medical.
Email Us at camden@atamed.sg for more
information.
Book your STD screening with us at 88770326


