Eczema Singapore: Testing & Treatment
Last updated: Feb 20, 2026
What Is Eczema?
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed
skin. It is often triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental
factors. Eczema is not contagious and can affect people of all ages, though
it is more commonly diagnosed in children. In Singapore, eczema affects approximately 1 in 5 children and 1 in 10
adults.
There are several types of eczema, each with distinct causes and patterns. Flare-ups can
vary in severity, but for many individuals, eczema leads to persistent discomfort,
sleep disturbances, and visible skin changes that may affect daily routines,
self-esteem, and overall quality of life.
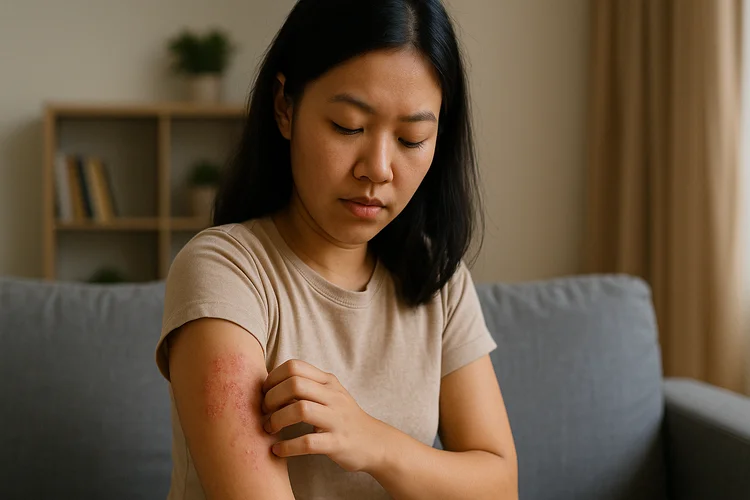

While eczema cannot be permanently cured, symptoms can often be managed effectively through consistent skincare, avoidance of known triggers, lifestyle adjustments, and appropriate medical treatment.
What Are the Symptoms of Eczema?
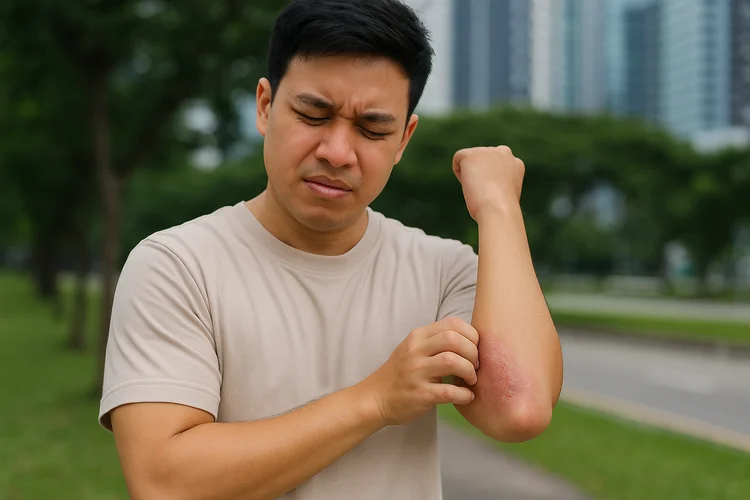
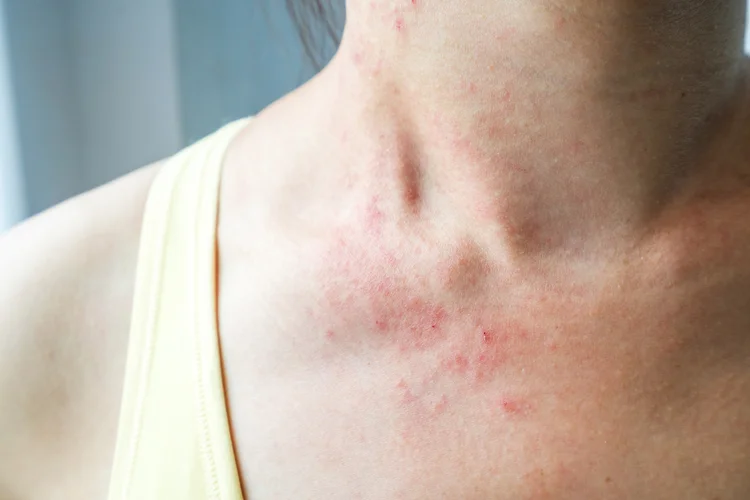

Eczema symptoms can vary in severity and appearance, depending on the individual and the specific type of eczema. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent itchiness, often more intense at night
- Dry, scaly, or cracked skin
- Red or inflamed skin
- Thickened or leathery skin from repeated scratching
- Skin discolouration during or after healing
- Oozing or crusting in more severe cases
These symptoms may affect the face, hands, neck, elbows, knees, or other parts of the body. Scratching can further damage the skin and increase the risk of secondary infections.
Eczema Causes
Eczema can develop from a combination of genetic, immunological, and environmental factors.
Individuals with eczema often have a compromised skin barrier, making the skin more susceptible to
moisture loss, irritants, allergens, and microbial exposure.
Common contributing factors include:
- Genetic Predisposition – A family history of eczema, asthma, or allergic rhinitis (hay fever) increases the likelihood of developing eczema.
- Irritants – Regular exposure to soaps, detergents, fragrances, or harsh chemicals can trigger or worsen symptoms.
- Environmental Allergens – Common triggers include dust mites, pet dander, mould, and pollen.
- Climate Factors – Hot and humid weather can aggravate flare-ups by increasing perspiration and skin irritation.
- Microbial Involvement – Skin colonisation or infection by bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus, can worsen eczema and impair healing.
- Stress and Hormonal Changes – Emotional stress or hormonal fluctuations may exacerbate symptoms or trigger flare-ups in some individuals.
Eczema Types
Different types of eczema present with varying symptoms and triggers, and some are more prevalent in Singapore’s humid climate or among specific age groups.
| Types | Description |
|---|---|
| Atopic Dermatitis | The most common form of eczema, especially in children. Presents as dry, itchy, inflamed patches on the face, neck, inner elbows, or behind the knees. Skin may thicken over time from repeated scratching. Often linked to a personal or family history of asthma, allergic rhinitis, or other atopic conditions. |
| Contact Dermatitis | It appears as red, itchy, and sometimes blistered or peeling skin after contact with irritants (e.g., soaps, detergents) or allergens (e.g., nickel, fragrances). The rash usually affects areas directly exposed, such as the hands or wrists. |
| Seborrhoeic Dermatitis | Usually presents as red, flaky, and greasy skin, most often on the scalp (dandruff), sides of the nose, eyebrows, and behind the ears. In infants, it may appear as a cradle cap. This type tends to recur and may be worsened by stress or changes in weather. |
| Asteatotic Eczema | Seen mostly in older adults, it presents as dry, cracked, and scaly skin, often described as resembling cracked porcelain. It typically affects the lower legs and worsens in low-humidity environments or with excessive washing. |
| Dyshidrotic Eczema | Characterised by small, fluid-filled blisters on the palms, sides of the fingers, or soles of the feet. These blisters are often intensely itchy and may cause peeling or thickening of the skin during healing. |
| Nummular Eczema | Manifests as round or oval-shaped itchy patches, often on the arms or legs. The lesions may be dry and scaly or oozing and crusted, and are usually triggered by very dry skin or skin injuries. |
How Is Eczema Diagnosed?
Eczema is generally diagnosed through a physical examination and detailed history of symptoms, lifestyle, and environmental exposure. It is typically a clinical diagnosis, meaning no specific test is needed in most cases.
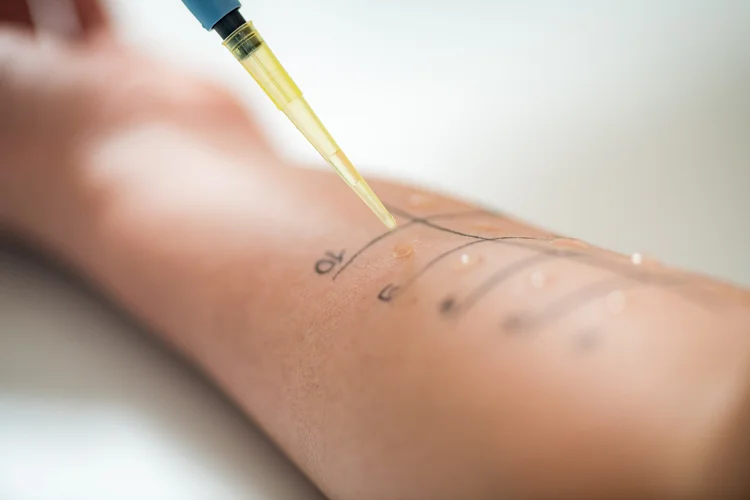
However, if symptoms are persistent, unclear, or if an allergic skin reaction is suspected, your doctor may recommend:
- Skin Prick Test – To identify specific allergens that may be triggering a reaction.
- Skin Swabs – To check for bacterial or fungal infections, especially if the skin appears oozing or crusted.
- Blood Tests – To assess underlying allergic tendencies or rule out other skin conditions with similar symptoms.
A clear diagnosis helps guide appropriate treatment and reduces the risk of recurrent flare-ups.
Eczema Treatment & Management
Eczema treatment involves a combination of medical therapies and lifestyle adjustments aimed at
relieving symptoms, reducing inflammation, repairing the skin barrier, and preventing flare-ups.
Treatment plans are typically tailored to the individual’s age, skin type, severity of symptoms, and
environmental triggers.
Common treatment options include:
| Treatment | Description & Purpose |
|---|---|
| Moisturisers (Emollients) | Moisturisers help lock in moisture and form a protective layer over the skin. Regular use prevents dryness, reduces itch, and supports skin barrier repair to minimise flare-ups. |
| Topical Corticosteroids | Anti-inflammatory creams or ointments used during flare-ups to reduce redness, swelling, and itching. They work by calming the body’s immune response in the affected areas. |
| Antihistamines | Oral medications that help relieve persistent itching, particularly at night. Reducing itch minimises scratching, which allows the skin to heal and reduces flare-up severity. |
| Antibiotics / Antifungals | Used topically or orally to treat skin infections that can complicate eczema. Clearing infection promotes healing and prevents worsening of symptoms. |
Other lifestyle measures to help manage eczema can include:
- Use gentle, fragrance-free soaps, cleansers, and detergents to minimise skin irritation and protect the skin barrier.
- Identify and avoid common triggers such as heat, sweat, dust mites, pet dander, certain fabrics, and specific foods when medically advised.
- Wear loose, breathable cotton clothing to reduce friction, overheating, and skin irritation.
- Take shorter, lukewarm showers to preserve natural skin oils and prevent dryness.
- Manage stress through mindfulness or regular exercise to help reduce eczema flare-ups.
Eczema Test & Treatment Price
At ATA Medical, we offer comprehensive diagnosis, allergen testing, and personalised treatment plans for eczema. Our fees are as follows:
| Test | Price* |
|---|---|
| Consultation | From $49.05 |
| Skin Prick Tests | |
| Single Allergen Skin Prick Test | From $54.50 |
| 12 Allergen Skin Allergy Package (12 Allergens) | $490.50 |
| Blood Tests | |
| Single Allergen Blood Test | From $67.58 |
| 59 Allergens Panel Comprehensive Blood Test | $739.02 |
|
Eczema Panel (11 Allergens) Cat Dander, Chicken, D. Pteronyssinus, Dog Dander, Egg White, Fish (Cod), Hazel Nut, Cow’s Milk, Peanut, Shrimp, Soya Bean |
$552.63 |
| Immunoglobulin G (Ig) Food Allergy/ Intolerance Tests (22 to 270 Food Panel Tests) | From $218 |
| Home Blood Test Service | Additional $54.50 |
^Prices last updated on Jan 28, 2026. While every effort is made to keep pricing information up to date, please contact our team to confirm the latest rates.
When Should You See a Doctor for Eczema?
You should consider seeing a doctor if:
- Symptoms persist despite regular use of moisturisers or over-the-counter treatments.
- The affected area becomes painful, swollen, or shows signs of infection (e.g., oozing, crusting).
- Eczema is disrupting sleep, daily routines, or quality of life.
- You experience frequent or severe flare-ups that are difficult to manage.
- You are unsure of your triggers or need support developing a long-term management plan.
Early medical attention can help prevent complications and improve symptom control.
Find an Eczema Doctor in Singapore
ATA Medical @ Tanjong Pagar
Nearest MRT: Tanjong Pagar Station (EW15)
Contact Number: 6223 0682
Email: hi@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed
ATA Medical @ Orchard
Nearest MRT: Orchard Boulevard Station (TE13)
Contact Number: 6223 0682
Email: camden@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed
ATA Medical @ Jurong
Nearest MRT: Jurong East MRT Station (NS1/EW24)
Contact Number: 6348 6292
Email: jurong@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed


