Audiometry Test
Last updated: Feb 20, 2026
| Test Name | Audiometry Test (Pure-Tone Audiometry – Air Conduction) |
| Purpose | Assesses hearing ability by measuring how well sounds at different volumes and pitches are detected, helping identify hearing loss and determine hearing thresholds. |
| Suitable For | Suitable for individuals with hearing changes, age-related concerns, ear-related symptoms, prolonged noise exposure, or workplace requirements for routine hearing checks. |
| Price | $54.50 NETT and inclusive of GST |
| Appointment Options |
Same-day appointment (subject to availability). Book via WhatsApp: 88750352 or email: camden@atamed.sg |
| Clinic Locations | Jurong: 21 Jurong Gateway Rd, #02-08 CPF Jurong Building, S608546 |
What Is an Audiometry Test?
An audiometry test is a hearing assessment that measures how well you detect sounds at
different volumes and pitches. It evaluates hearing thresholds (the quietest sounds you
can hear), identifies possible hearing loss, and indicates whether
further testing or treatment may be required.
An audiometry test is often considered when there are hearing changes that may be linked to ageing,
prolonged noise exposure, or underlying ear conditions.
During the test, you respond to tones or speech delivered through specialised equipment such as an
audiometer and calibrated headphones, indicating whenever
you hear a sound so your hearing levels can be measured accurately across different pitches and
volumes.
Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is categorised based on which part of the hearing system is affected:
- Conductive hearing loss arises from problems in the outer or middle ear, such as wax build-up, fluid, or eardrum issues.
- Sensorineural hearing loss results from changes in the inner ear or auditory nerve, commonly linked to ageing or noise exposure, and may also occur with medical disorders such as Ménière's disease.
- Mixed hearing loss includes features of both conductive and sensorineural loss.

Who Should Consider an Audiometry Test?
An audiometry test can be considered by individuals who notice changes in hearing, have ongoing ear-related symptoms, or require routine hearing assessments for work or health monitoring. This includes those who:
- Struggle to hear conversations, especially in noisy places
- Notice muffled or unclear sounds
- Experience ringing, buzzing, or discomfort in the ears
- Experience age-related changes that affect hearing clarity
- Work in environments with prolonged or excessive noise exposure
- Have a history of chronic or recurrent ear infections
- Are required by their employers to undergo regular hearing checks as part of workplace safety programmes
What Happens During an Audiometry Test?
An audiometry test involves a series of listening tasks that assess hearing across
different tones, pitches, and speech patterns.
These tasks may include pure-tone audiometry (air conduction), bone conduction
testing, and speech audiometry. Not all components are required for every
individual, and the tests performed depend on age, symptoms, and the purpose of the
assessment.
You usually sit in a quiet room with headphones while sounds are played through an
audiometer (a device that produces controlled tones and speech for hearing assessment), and
you indicate whenever a tone or word is heard.

Pure-Tone Audiometry (Air Conduction)
Pure-tone audiometry measures the quietest sounds that can be heard at different pitches using headphones. A series of beeps is played at various frequencies and volumes, and the softest ones detected are recorded to form the basis of the audiogram.
Bone Conduction Testing
Bone conduction testing assesses how well the inner ear receives sound by sending gentle vibrations through a small device placed behind the ear. This test is usually performed when air conduction results suggest a possible hearing issue, as it helps determine whether any hearing loss is related to the outer or middle ear (conductive) or the inner ear or hearing nerve (sensorineural).
Speech Audiometry
Speech audiometry evaluates how clearly spoken words are understood at different volumes. Words or sentences are played through the headphones, and the responses provide information about speech clarity and overall hearing function.
What Do Audiometry Results Mean?
Audiometry findings are presented in different ways depending on the type of test performed:
| Type of Audiometry | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Air Conduction | Thresholds are plotted on an audiogram to show whether hearing falls within a normal range or reflects mild, moderate, or more severe loss. |
| Bone Conduction | Thresholds are marked on the same audiogram to indicate whether changes arise from the outer or middle ear (conductive) or from the inner ear or hearing nerve (sensorineural). |
| Speech Audiometry | Speech understanding is shown as a percentage score based on how many spoken words are correctly repeated at different loudness levels. |
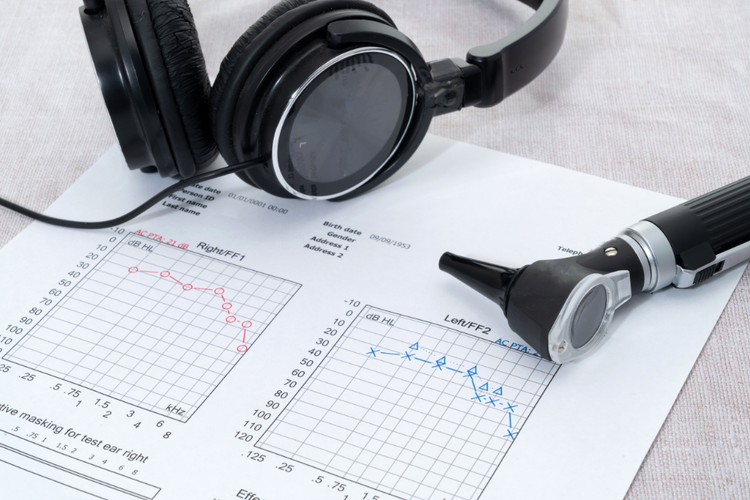
Your doctor will review these findings with you and explain whether further evaluation or specialised care is recommended.
How Much Does An Audiometry Test Cost?
At ATA Medical, we provide pure-tone audiometry (air conduction) and bone conduction at our Jurong clinic as part of our broader health assessment services. The prices for this test and other related assessments are as follows:
| Test | Price* |
|---|---|
| Consultation | From $49.05 |
| Pure-Tone Audiometry (Air Conduction, Bone Conduction if required) | $54.50 |
| Retinal Imaging | From $54.50 |
| Digital Brain Function Screen (DBFS) | From $38.15 |
^Prices last updated on Jan 28, 2026. While every effort is made to keep pricing information up to date, please contact our team to confirm the latest rates.
We also offer audiometry testing at a corporate level, along with other workplace health
services provided by our Designated Workplace Doctors
(DWD).
For a more comprehensive review of your health, you may also consider our health screening
packages.
How Long Does an Audiometry Test Take?
At our clinic, the audiometry test itself typically takes about 3 to 5 minutes to
complete during off-peak hours, excluding consultation time. For statutory testing, a consultation
is not required.
Contact
us to find the most suitable time to book your appointment.
How to Prepare for an Audiometry Test?
There are no specific compulsory steps before an audiometry test, but certain measures can help ensure more accurate and reliable results. These may include:
- Avoiding loud noise for at least 12 to 24 hours before the test
- Informing the doctor of any ear infections, recent ear procedures, or ear-related symptoms
How to Book an Appointment For an Audiometry Test?
ATA Medical @ Jurong
Nearest MRT: Jurong East MRT Station (NS1/EW24)
Contact Number: 6348 6292
Email: jurong@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed


