What Is Cancer Screening?
Cancer screening involves medical tests designed to detect cancer early,
often before symptoms appear. These tests examine cells for abnormal changes such as
dysplasia (irregular cell growth), atypical
hyperplasia (an unusual increase in cell numbers), or genetic mutations that may
increase cancer risk.
Identifying these early changes enables the detection of precancerous conditions or
cancer in its initial stages, when treatment is most effective.
Cancer Rate in Singapore
In Singapore, cancer remains a major health concern, with an average of 46 new diagnoses
daily and 16 cancer-related deaths each day between 2017 to 2021.
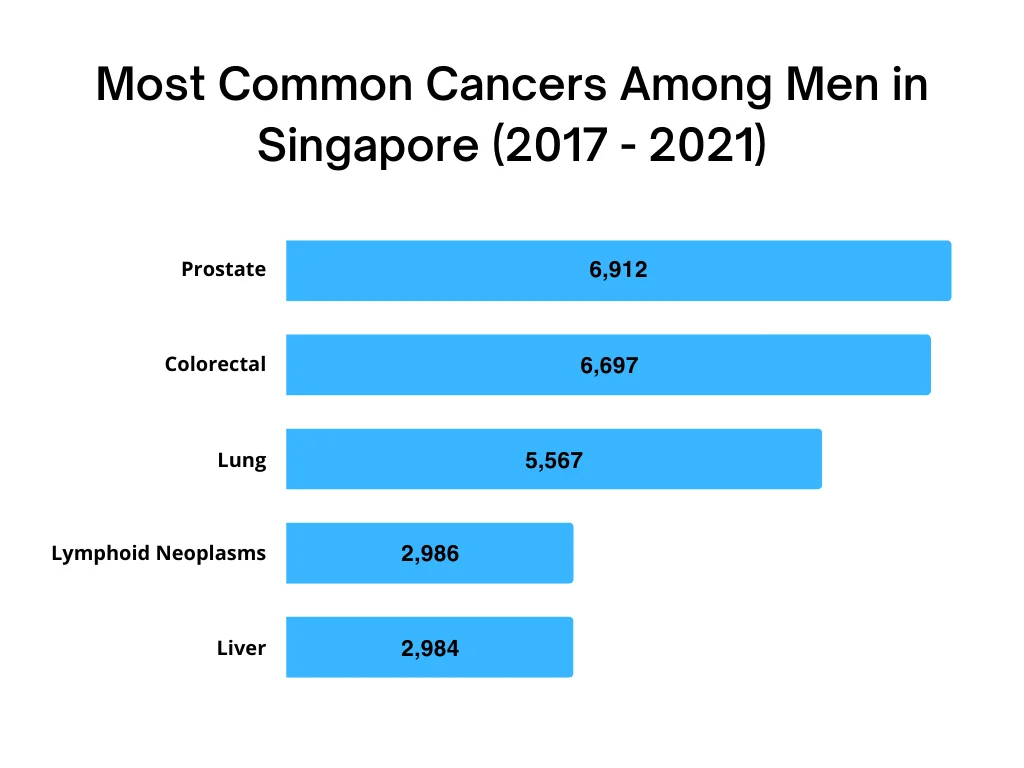
Among men, the three most common cancers are:
- Prostate cancer: 6,912 cases (16.8% of all male cancers)
- Colorectal cancer: 6,697 cases (16.3%)
- Lung cancer: 5,567 cases (13.5%)
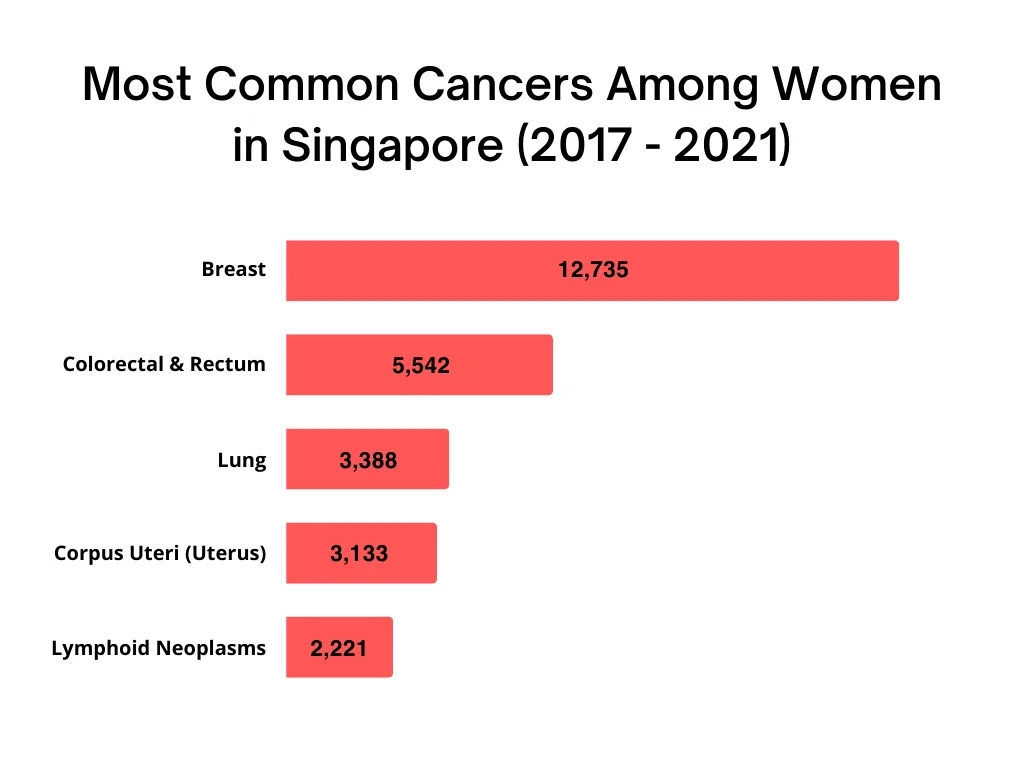
Among women, the three most common cancers are:
- Breast cancer: 12,735 cases (29.7% of all female cancers)
- Colorectal cancer: 5,542 cases (12.9%)
- Lung cancer: 3,388 cases (7.9%)
Why Is Cancer Screening Important?
Screening is essential in improving treatment success by identifying cancer at its earliest, most treatable stage. Certain types of cancer, such as breast, cervical, and colorectal cancer, have much higher survival rates when found early. Besides detecting existing cancer, screening can also identify precancerous changes, enabling preventive actions that may stop cancer from developing.
What Types of Cancer Screening Are Available?
Cancer screening methods vary based on how they detect abnormal changes in the body. These tests fall into three main categories: laboratory tests, imaging scans, and direct tissue examinations. Each method serves a specific purpose in detecting cancerous or precancerous conditions.
Laboratory and Biomarker Tests
These tests analyse blood, urine, or stool samples to detect cancer-related markers or abnormal cell changes. Some are used for early detection, while others help assess risk or monitor cancer progression. Common examples include:
- Blood tests for tumour markers
- HPV testing for cervical cancer
- Faecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT) for colorectal cancer
- Liquid biopsy to detect circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA)
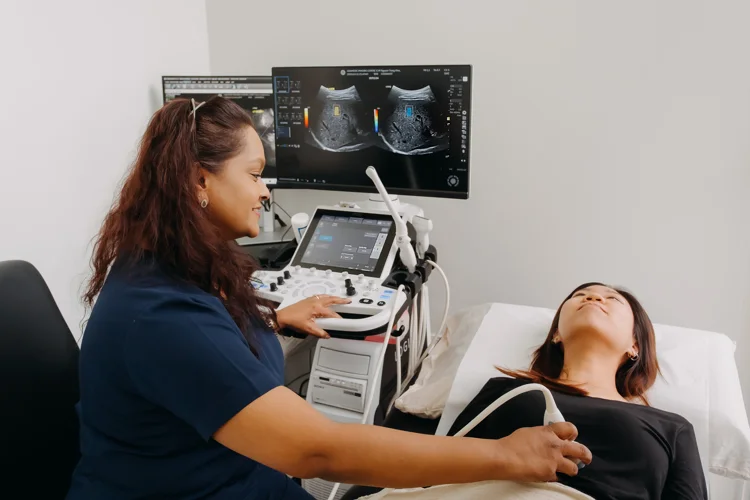
Imaging-Based Screening Tests
These tests use non-invasive scanning technology to detect tumours or abnormal tissue changes. They are commonly used as first-line screening tools for cancers affecting solid organs and may also guide further diagnostic procedures. Examples include:
- Mammograms for breast cancer
- Low-dose CT scans for lung cancer
- Liver ultrasound for liver cancer
Direct Examination Tests
These tests allow doctors to visually inspect tissues or collect samples for microscopic analysis. They are typically performed when screening tests suggest abnormalities or when a more detailed evaluation is necessary. Unlike screening tests, biopsies provide a definitive diagnosis by confirming whether cancer is present. Examples include:
- Colonoscopy for colorectal cancer
- Endoscopy for oesophageal and stomach cancer
- Biopsy for suspicious tissue growths
How Often Should You Go for Cancer Screening?
The recommended frequency of cancer screening depends on factors such as age, gender, medical history, and individual risk factors. Below are common cancers screened and their recommended tests:
| Screening Test | Description | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Cervical Cancer | ||
| PAP Smear | A small sample of cervical cells is collected using a soft brush and examined under a microscope to detect precancerous or abnormal cell changes in the cervix. | Females aged 25 to 29: Every 3 years |
| HPV Test | A cervical cell sample is tested for high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) strains, which may cause cervical cancer. This test can be performed using the same sample as a PAP smear. | Females aged 30 and above: Every 5 years |
| Breast Cancer | ||
| Mammogram | A low-dose X-ray scan compresses the breast tissue to capture detailed images, detecting lumps or abnormal growths. | Females aged 40 and above: Every year |
| Prostate Cancer | ||
| Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test | A blood test measures PSA levels, which may be elevated in prostate cancer or other prostate conditions. | High-risk males aged 50 and above |
| Colorectal Cancer | ||
| Stool Occult Blood Test (Faecal Immunochemical Test) | A stool sample is tested for microscopic traces of blood, which requires further evaluation to test for polyps, inflammation, gastrointestinal conditions or colorectal cancer. | All individuals aged 50 and above: Every year |
| Colonoscopy | A flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the colon to check for polyps or abnormal growths. It can also be used to remove polyps or precancerous lesions. | All individuals aged 50 and above: Every 10 years (or earlier if at high risk) |
| Lung Cancer | ||
| Low-dose CT scan | A non-invasive imaging test that uses low-dose radiation to scan the lungs for tumours or abnormalities. | High-risk individuals aged 55 and above: Every year |
| Liver Cancer | ||
| Liver Function Tests | A blood test that measures liver enzyme levels, which can indicate liver disease or dysfunction. | Individuals at risk |
| Ultrasound | A non-invasive scan using sound waves to detect liver tumours or abnormalities. | Individuals at risk |
Screening for breast, cervical, and colorectal cancer is recommended under the Health Promotion Board (HPB) Screen for Life programme. For other cancers, screening recommendations depend on individual risk factors, so it is best to consult a doctor to determine the most appropriate screening schedule for you.
How Much Does Cancer Screening Cost in Singapore?
At ATA Medical, we offer a range of cancer screening tests with the following price list:
| Screening Test | Price* |
|---|---|
| Consultation | From $49.05 |
| Cervical Cancer | |
| PAP Smear | From $0 |
| HPV Test | From $0 |
| Breast Cancer | |
| Mammogram | $239.80 |
| Ultrasound Breast + Mammogram | $327 |
| Prostate Cancer | |
| Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test | $38.15 |
| Colorectal Cancer | |
| Stool Occult Blood Test (Faecal Immunochemical Test) | $27.25 |
| Colonoscopy | From $2398 |
| Lung Cancer | |
| Low-dose CT Scan | $436 |
| Liver Cancer | |
| Liver Function Tests | From $30.52 |
| Ultrasound Liver (Full HBS) | $196.20 |
| Other Tests | |
| LucenceINSIGHT™ Liquid Biopsy Cancer Screening (From 6 Cancers) | From $654 |
^Prices last updated on Mar 02, 2026. While every effort is made to keep pricing information up to date, please contact our team to confirm the latest rates.
We also offer additional diagnostic tests such as X-rays, MRI, and CT scans for further evaluation if needed.
Subsidies and MediSave Claims
As a CHAS-accredited clinic, we offer subsidies for eligible cancer screenings under Screen for Life (SFL). Selected procedures may also be claimable via MediSave, subject to eligibility criteria. Please contact us for more details on financing options and eligibility.
Comprehensive Health Screening Packages
For a more in-depth health assessment, consider our comprehensive health screening packages, which can include multiple tests to screen for various cancers and other medical conditions.
Why Choose ATA Medical?







Making a Difference Together
At ATA Medical, we strive to make a meaningful impact on every patient's health. With over 150,000 patients served, we are dedicated to fostering trust and enhancing well-being across our community.
Patients
Health Screening Tests
Corporate Screenings
Delivering Care Patients Appreciate
What to Expect
FAST RESULTS
We strive to deliver your results within 7 working days.
MINIMUM WAITING TIME
Our patient-oriented processes ensure your waiting time is kept to a minimum.
Friendly Service
Service is a top priority for us at ATA Medical.
Email Us at camden@atamed.sg
for More Information.
Book Your Cancer Screening With Us at 88838892.

