Diabetic Foot Screening
Last updated: Feb 20, 2026
What Is Diabetic Foot Screening?
Diabetic foot screening is a preventive health check aimed at detecting early signs of foot complications in people with diabetes. This physical examination assesses for infections and sores, blood flow issues, and nerve damage (neuropathy).
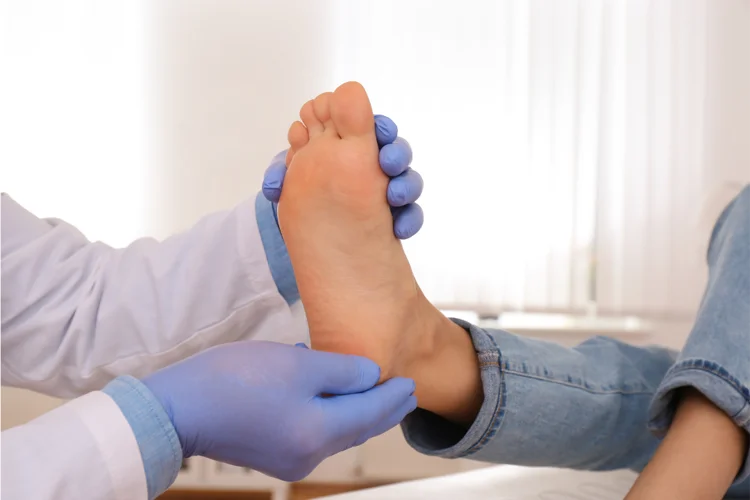

These problems, if left untreated, can escalate into serious complications. In Singapore, diabetic foot-related complications account for 20% of emergency admissions, and people with diabetes are 20 times more likely to face amputation than those without the condition.
Regular screening plays a vital role in catching these issues early, when they are most treatable, helping to reduce the risk of serious outcomes.
What Are Diabetic Foot Ulcers?
Diabetic foot ulcers are open sores or wounds that usually form on the legs or the feet. They develop when high blood sugar levels damage nerves and blood vessels, impairing the body’s ability to heal.
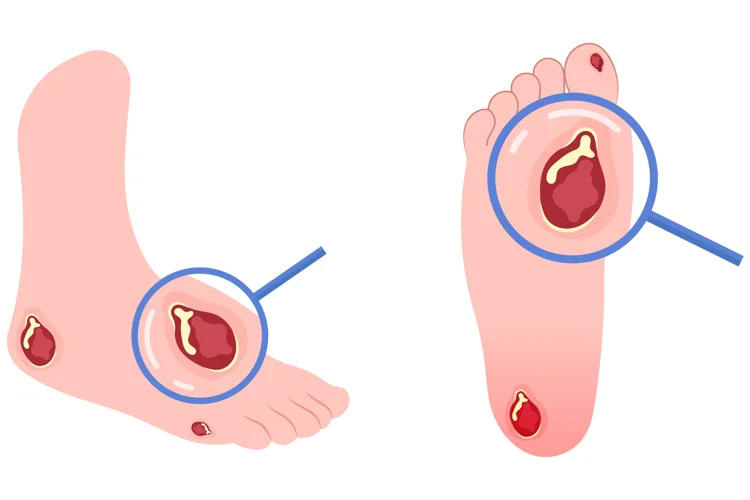
Early Stage Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Diabetic foot ulcers progress through various stages, from being at risk to developing gangrene. Early noticeable signs typically include:
- Unexplained pain or discomfort in the foot
- Redness, swelling, or warmth in the affected area
- Blisters, calluses, or changes in skin colour
- Open wounds that take a long time to heal, or an unpleasant odour or discharge from the wound
If you have diabetes and experience any of these signs, it's important to see a doctor immediately.
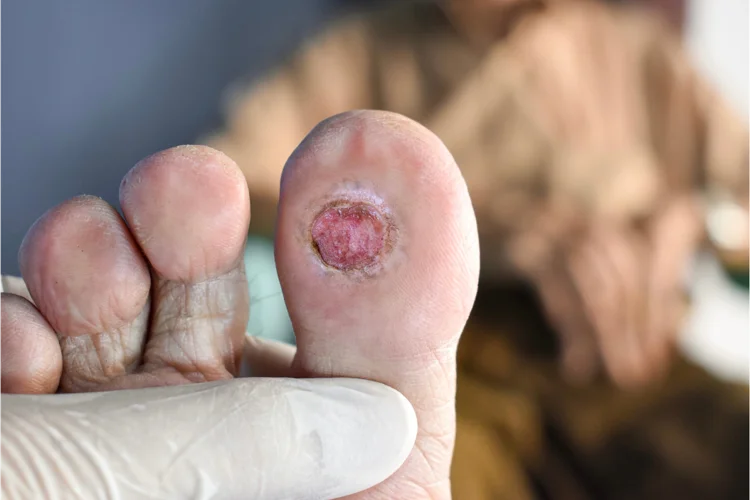
Causes & Contributors to Diabetic Foot Ulcers
In addition to diabetes impairing the body’s ability to heal, several factors contribute to the risk of diabetic foot ulcers, including:
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Loss of sensation in the feet, which can prevent you from noticing injuries or pressure points.
- Poor Circulation: Restricted blood flow due to damaged blood vessels, making it harder for wounds to heal.
- Foot Deformities: Changes in foot structure or shape, which increase pressure on certain areas, leading to ulcers.
- Inadequate Foot Care: Failure to maintain proper foot hygiene or wear suitable footwear can also increase the risk of ulcers.
Who Should Get a Diabetic Foot Screening?
People with diabetes are advised to have diabetic foot screenings at least once a year. However, individuals with higher risk factors may need more frequent screenings, typically every 3 to 6 months. These higher-risk factors include:
- A history of foot ulcers or amputations
- Nerve damage or loss of sensation in the feet
- Poor blood circulation or peripheral artery disease
- Foot deformities such as hammertoes or bunions
It is best to consult your doctor for personalised advice on the appropriate screening frequency.
Cost of Diabetic Foot Screening in Singapore
At ATA Medical, we provide diabetes foot screening and other related tests and treatments at the following prices:
| Tests | Price* |
|---|---|
| Consultation | From $49.05 |
| Diabetes-Related Complications Screening | |
| Diabetic Foot Screening | $38.15 |
| Diabetic Retinal Photography | $54.50 |
| Diabetes Blood Glucose Tests | |
| Fasting Blood Glucose (FBG) Test | $10.90 |
| Glycated Haemoglobin (HbA1c) Test | $27.25 |
| Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) | $27.25 |
| Fasting Insulin Test | $66.49 |
^Prices last updated on Jan 28, 2026. While every effort is made to keep pricing information up to date, please contact our team to confirm the latest rates.
CHAS, Merdeka Generation (MG), and Pioneer Generation (PG) subsidies are available for diabetes-related complications screenings. Please contact us for more information on eligibility.
Where to Go for Diabetic Foot Screening in Singapore
ATA Medical is conveniently located at two different locations:
- Tanjong Pagar Medical Clinic (Closest MRT: Tanjong Pagar EW15)
- Orchard Clinic (Closest MRT: Orchard Boulevard TE13)
How Do I Book a Diabetic Foot Screening Appointment?
ATA Medical @ Tanjong Pagar
Nearest MRT: Tanjong Pagar Station (EW15)
Contact Number: 6223 0682
Email: hi@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed
ATA Medical @ Orchard
Nearest MRT: Orchard Boulevard Station (TE13)
Contact Number: 6223 0682
Email: camden@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed
ATA Medical @ Jurong
Nearest MRT: Jurong East MRT Station (NS1/EW24)
Contact Number: 6348 6292
Email: jurong@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed


