Diabetic Retinal Photography
Last updated: Feb 20, 2026
What Is Diabetic Retinal Photography?
Diabetic retinal photography is a non-invasive screening technique used to detect and monitor diabetic retinopathy in individuals with diabetes. This procedure involves capturing high-resolution images of the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye, to identify early signs of diabetic eye disease.
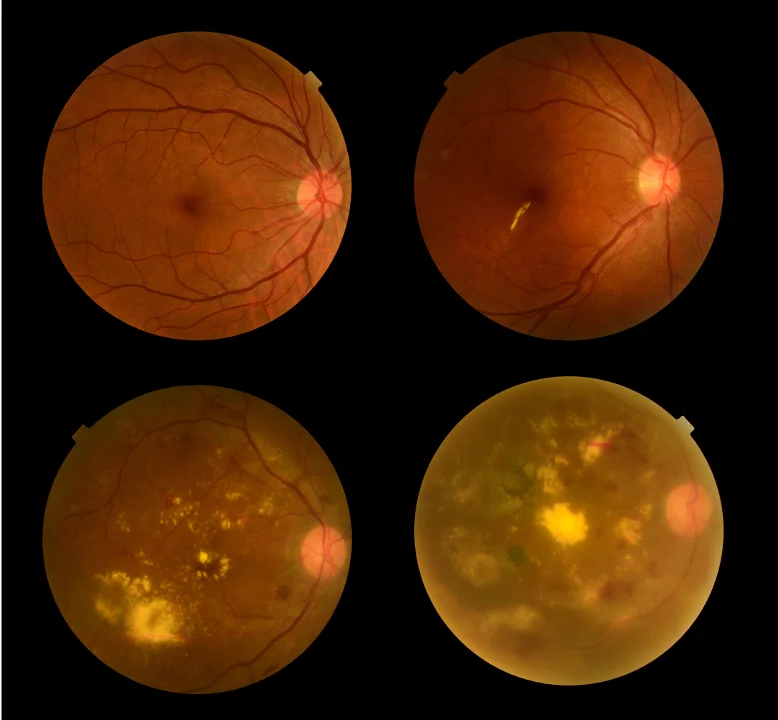
What Is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is an eye condition caused by high blood sugar levels damaging the retina's blood vessels. This damage can lead to leakage, swelling, and abnormal new blood vessel growth, potentially leading to vision loss. It is a leading cause of blindness among working-age adults and can progress silently in its early stages.

In Singapore, about 10% of adults aged 18 to 69 have diabetes. Among them, roughly 30% develop diabetic retinopathy, and of those, around 10% progress to the more severe stages where their vision is at risk. Early detection of changes in the retinal blood vessels can help prevent vision loss through timely intervention.
Types of Diabetic Retinopathy
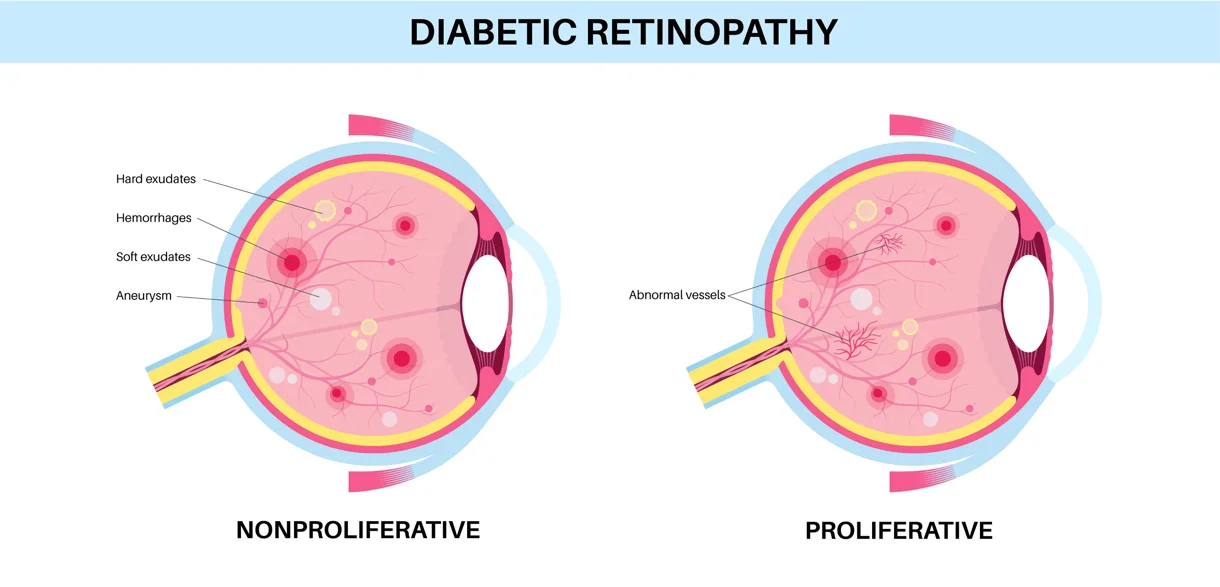
Diabetic retinopathy is classified into two main stages:
- Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR): This early stage is characterised by changes in retinal blood vessels such as swelling, microaneurysms (small bulges in blood vessels), and fluid leakage. It is often symptomless but can lead to more severe forms if untreated.
- Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR): This advanced stage occurs when the retina becomes deprived of oxygen due to blocked blood vessels. To compensate, abnormal new blood vessels grow, which are fragile and prone to bleeding, potentially causing vision loss or blindness.
Diabetic Retinopathy Symptoms
In its early stages, diabetic retinopathy may not show any signs. However, as the condition progresses, individuals may experience symptoms such as:
- Blurred or fluctuating vision
- Dark spots or floaters
- Difficulty seeing colours
- Partial or total loss of vision
Complications of advanced diabetic retinopathy can include:
- Diabetic Macular Edema (DME): Swelling of the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision, which can lead to significant vision loss.
- Neovascular Glaucoma: New, abnormal blood vessels grow and block fluid drainage from the eye, increasing eye pressure and potentially leading to optic nerve damage and vision loss.
- Retinal Detachment: Scar tissue forms and pulls the retina away from the back of the eye, causing severe visual impairment or blindness if untreated.

Causes & Contributors to Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is primarily caused by prolonged high blood sugar levels, which damage retinal blood vessels over time. Other contributors include:
- Poor blood sugar control
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Long duration of diabetes (the longer you have diabetes, the higher your risk)
- Smoking
How Does Diabetic Retinal Photography Work?
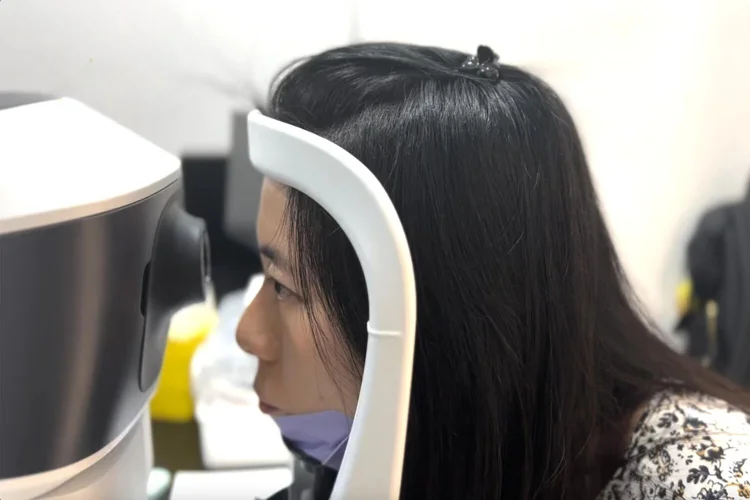

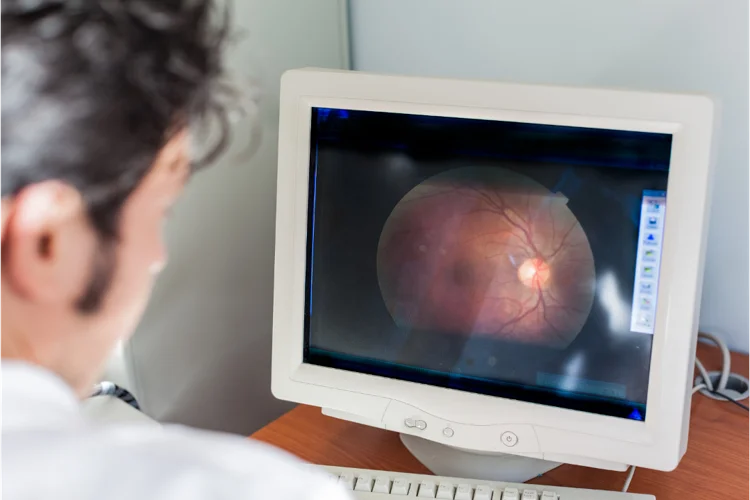
Retinal photography uses a specialised camera to capture detailed images of the retina. During the procedure, the patient may need to have their pupils dilated with eye drops to allow a clearer view of the retina. The images are then reviewed by a specialist to check for signs of diabetic retinopathy, such as swelling, bleeding, or abnormal blood vessel growth.


Who Is Diabetic Retinal Photography Recommended for?
Diabetic retinal photography is recommended for all individuals with diabetes, regardless of whether they have symptoms of retinopathy. The frequency of screening depends on factors such as the type of diabetes and how well it is managed. In general, annual retinal photography is advised for patients with diabetes to monitor for early signs of retinopathy and prevent complications like vision loss.
Cost of Diabetic Retinal Photography in Singapore
At ATA Medical, we offer diabetes retinal photography and a range of eye screenings and diabetes-related tests at the following prices:
| Tests | Price* |
|---|---|
| Consultation | From $49.05 |
| Diabetes-Related Complications Screening | |
| Diabetic Retinal Photography | $54.50 |
| Diabetic Foot Screening | $38.15 |
| Eye Screenings | |
| Retinal Photography + Tonometry | $81.75 |
| Visual Acuity (Far and Near) + Colour Vision + Retinal Photography + Tonometry | $106.82 |
| Diabetes Blood Glucose Tests | |
| Fasting Blood Glucose (FBG) Test | $10.90 |
| Glycated Haemoglobin (HbA1c) Test | $27.25 |
| Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) | $27.25 |
| Fasting Insulin Test | $66.49 |
^Prices last updated on Jan 28, 2026. While every effort is made to keep pricing information up to date, please contact our team to confirm the latest rates.
CHAS, Merdeka Generation (MG), and Pioneer Generation (PG) subsidies are available for diabetes-related complications screenings. Please contact us for more information on eligibility.
Where to Go for Diabetic Retinal Photography in Singapore
ATA Medical is conveniently located at two different locations:
- Tanjong Pagar Medical Clinic (Closest MRT: Tanjong Pagar EW15)
- Orchard Clinic (Closest MRT: Orchard Boulevard TE13)
How Do I Book a Diabetic Retinal Photography Appointment?
ATA Medical @ Tanjong Pagar
Nearest MRT: Tanjong Pagar Station (EW15)
Contact Number: 6223 0682
Email: hi@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed
ATA Medical @ Orchard
Nearest MRT: Orchard Boulevard Station (TE13)
Contact Number: 6223 0682
Email: camden@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed
ATA Medical @ Jurong
Nearest MRT: Jurong East MRT Station (NS1/EW24)
Contact Number: 6348 6292
Email: jurong@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed


