What Is a Skin Rash?
A skin rash is any abnormal change in your skin's colour, texture, or appearance, commonly showing up as redness, bumps, blisters, dry patches, or scaly skin. Skin rashes have many possible causes, including allergic reactions, viral or bacterial infections, contact with irritants, heat, and underlying health conditions such as eczema or psoriasis. They may appear suddenly or develop gradually, and can affect a small area or spread across the body.
What Are the Common Symptoms of a Skin Rash?
Skin rashes can vary in appearance, size, texture, and distribution. Common symptoms include:
Redness or Discolouration
The affected area may appear pink, red, purplish, or darker than the surrounding skin, depending on skin tone. The intensity can range from faint to deep and may blend into normal skin.
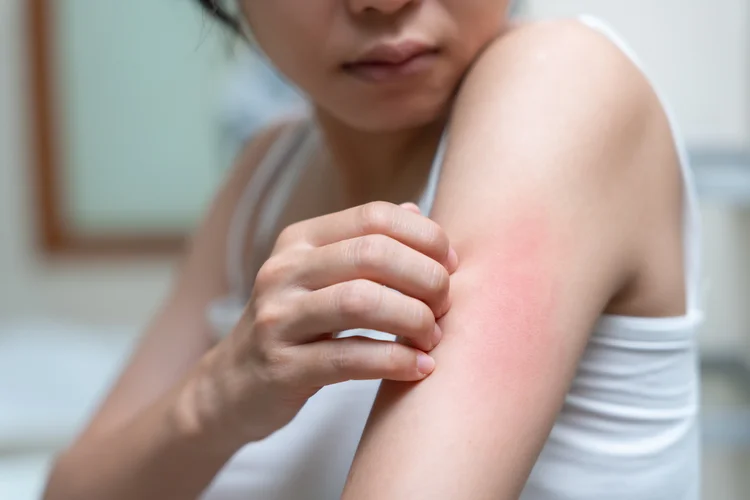

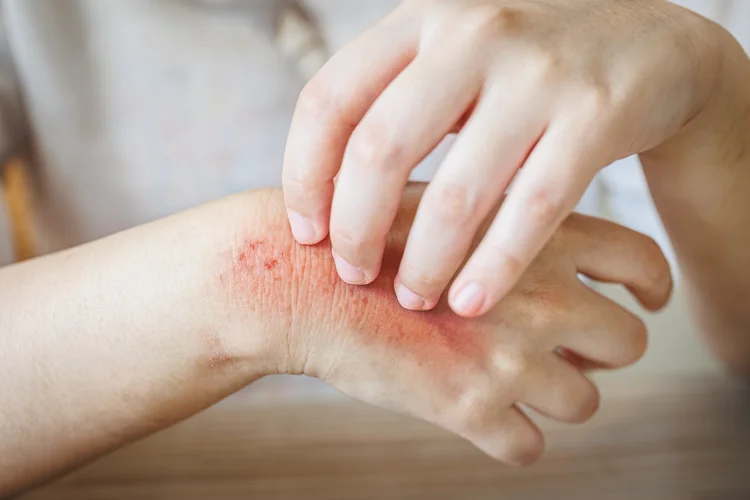
Itching or Irritation
Rashes may cause mild to intense itching, sometimes accompanied by tingling or burning. Hives (urticaria) often present as intensely itchy welts that can change shape and size rapidly.
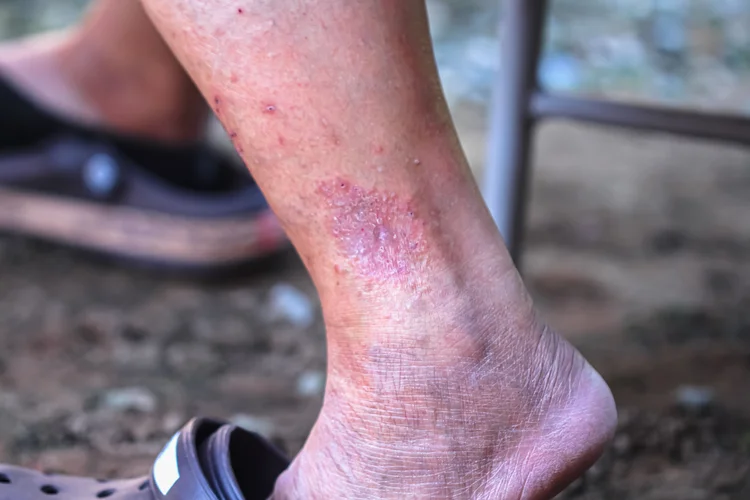
Dry, Scaly, or Flaky Patches
Some rashes present as rough, cracked, or peeling skin. Fungal infections often have a distinct scaly border with central clearing, forming a ring-like pattern.
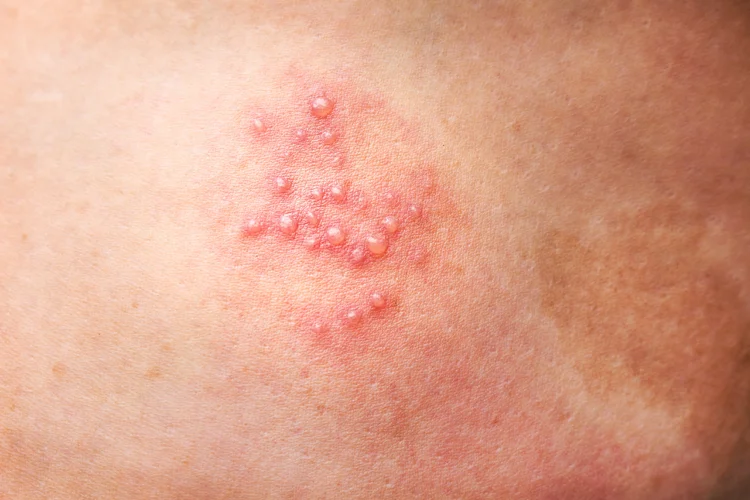
Raised Bumps or Blisters
Rashes can include papules (small solid bumps), pustules (pus-filled bumps), vesicles (fluid-filled blisters), or wheals (raised, swollen areas seen in hives). Blisters may be clear or cloudy, depending on their contents.
Swelling or Thickened Skin
The affected area may feel puffy, firm, or thickened, with the skin appearing stretched or elevated. Chronic irritation can cause lichenification, where the skin thickens and develops pronounced lines.
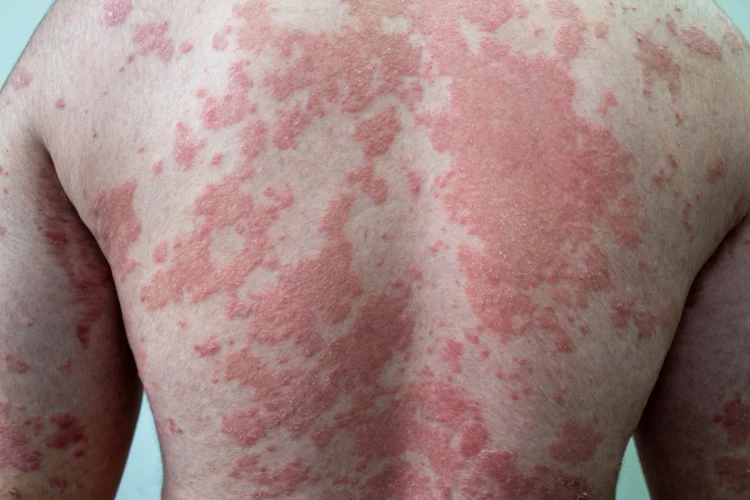
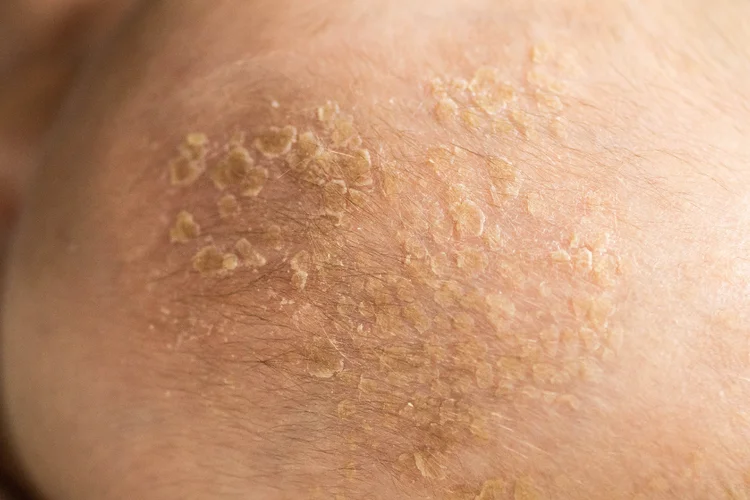
Oozing, Crusting, or Scaling
Some rashes may release fluid or form yellowish or brown crusts as they heal. This is often seen in weeping eczema or infected rashes.
Distinct Borders or Shapes
Some rashes follow specific patterns. Fungal infections like ringworm form
circular patches with a raised, scaly edge, while viral rashes, such as
measles, can spread in a lace-like or blotchy pattern.
While many rashes are temporary and resolve on their own, persistent,
worsening, or unusual rashes should be evaluated by a doctor.
What Causes Skin Rashes?
Skin rashes can arise from a variety of physiological, immunological, and environmental factors, including:
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Irritant Contact Dermatitis | Direct exposure to chemicals, soaps, detergents, or synthetic fabrics weakens the skin barrier, causing redness, dryness, and inflammation. |
| Allergic Reactions | The immune system overreacts to allergens like pollen, pet dander, certain foods, or medications, leading to itchy rashes, hives, or contact dermatitis. |
| Heat and Sweat Retention | Blocked sweat ducts, especially in humid conditions, trap perspiration under the skin, forming small, red, itchy bumps (heat rash/miliaria). |
| Infections | Bacterial (e.g., impetigo, cellulitis), viral (e.g., chickenpox, measles), and fungal (e.g., ringworm, athlete’s foot) infections can cause rashes with blisters, pus, or scaling. Some sexually transmitted infections (STIs), like syphilis and herpes, may also cause distinctive rashes. |
| Autoimmune and Inflammatory Conditions | Chronic immune dysregulation in conditions such as psoriasis, eczema (atopic dermatitis), and lupus leads to persistent inflammation, scaling, and skin thickening. |
| Insect Envenomation and Parasitic Infestations | Bites from mosquitoes, bedbugs, or mites trigger localised swelling, itching, and red bumps due to the body's immune response to saliva or venom. Persistent scratching can break the skin, increasing the risk of secondary infections, where bacteria enter the wound. |
| Drug-Induced Exanthems | Certain medications, including antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and anticonvulsants, may trigger widespread rashes, hives, or severe hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., Stevens-Johnson Syndrome). |
How Is a Skin Rash Diagnosed?
Diagnosing skin rashes involves assessing their appearance, distribution, associated symptoms, and recent exposures to allergens, medications, or infections. In some cases, additional tests may be required, including:
- Skin Scraping or Swab Tests – Detects bacterial or fungal infections by analysing skin cells or fluid under a microscope.
- Allergy Testing (Patch or Skin Prick Tests) – Identifies allergic triggers by applying allergens to the skin (patch test) or introducing small amounts under the skin (skin prick test) to check for reactions like redness or swelling.
- Blood Tests – Helps diagnose autoimmune conditions and systemic infections. Allergen blood tests (e.g., IgE tests) can also detect allergic sensitivities.
- Biopsy – A small skin sample is extracted and examined under a microscope to confirm or rule out specific skin disorders.
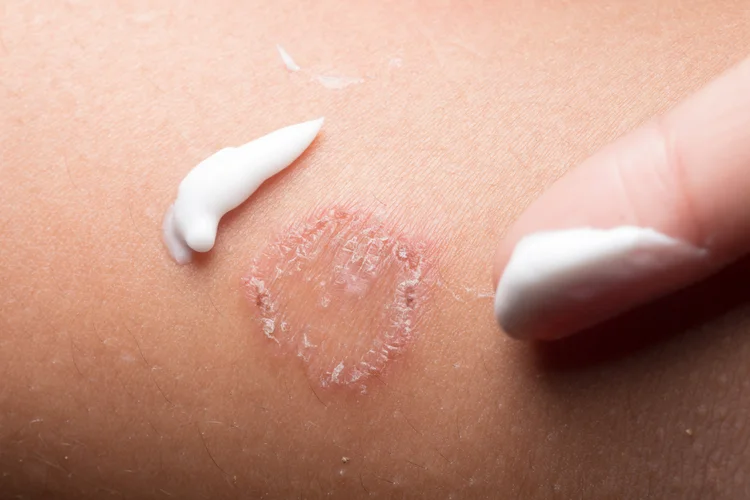
How Are Skin Rashes Treated?
The treatment of skin rashes depends on their underlying cause and severity. Common approaches include:
| Treatment Approach | Description |
|---|---|
| Topical Treatments |
|
| Oral Medication |
|
| Lifestyle Adjustments |
|
When Should You See a Doctor for a Skin Rash?
Seek medical attention if a rash:
- Spreads rapidly or worsens over time, especially if it covers a large area or changes in appearance.
- Is accompanied by fever, swelling, or pain, which may indicate an infection or an underlying medical condition.
- Develops into blisters, ulcers, or open sores, increasing the risk of secondary infections or complications.
- Does not improve with over-the-counter treatments, suggesting a persistent or undiagnosed cause.
- Appears after starting a new medication, as this could be a sign of a drug reaction, which may require immediate medical evaluation.
Conclusion
Skin rashes are common and can range from mild irritations to signs of underlying
medical conditions. While many rashes resolve with simple care, others may
persist, spread, or cause discomfort that interferes with daily life.
Recognising the symptoms and potential causes can help you determine when to seek
medical attention and how to manage your skin effectively.
If your rash is worsening, spreading, or accompanied by pain, fever, or other
unusual symptoms, schedule
a consultation with a doctor for further evaluation and appropriate
treatment.
Why Choose ATA Medical?







Making a Difference Together
At ATA Medical, we strive to make a meaningful impact on every patient's health. With over 150,000 patients served, we are dedicated to fostering trust and enhancing well-being across our community.
Patients
Health Screening Tests
Corporate Screenings
Delivering Care Patients Appreciate
What to Expect
FAST RESULTS
We strive to deliver your results within 7 working days.
MINIMUM WAITING TIME
Our patient-oriented processes ensure your waiting time is kept to a minimum.
Friendly Service
Service is a top priority for us at ATA Medical.
Email Us at camden@atamed.sg
for More Information.
Book Your Skin Rash Treatment With Us at 88770326.

