A common misconception is that people with diabetes should avoid fruits
entirely because of their natural sugar content. In reality, fruits
are recommended as part of a balanced diet and, when chosen
wisely, can support effective diabetes management.
Fruits provide valuable nutrients including vitamins and minerals, dietary
fibre for digestion, and antioxidants for heart health. Good blood
sugar control through proper diet can also help reduce the risk of
diabetes-related complications such as foot
ulcers and retinopathy.
When including fruits in their diet, those with diabetes should opt for
varieties with a low glycaemic index and practise portion
control.

What Is Glycemic Index (GI) & Glycemic Load (GL)?
The glycemic index (GI) ranks carbohydrates based on how quickly they raise blood sugar levels, on a scale from 0 to 100. Low-GI foods (below 56) cause slower, steadier increases in blood sugar, while high-GI foods (above 70) lead to faster spikes. The glycemic load (GL)provides a more practical measure by considering both the GI of the food and the typical portion size, helping to assess the overall impact on blood sugar. A low GL is ideal for managing diabetes, while a high GL may cause significant blood sugar fluctuations.
- Low GL: 10 or less
- Medium GL: 11–19
- High GL: 20 or more
Best Low GI Fruits for Diabetics
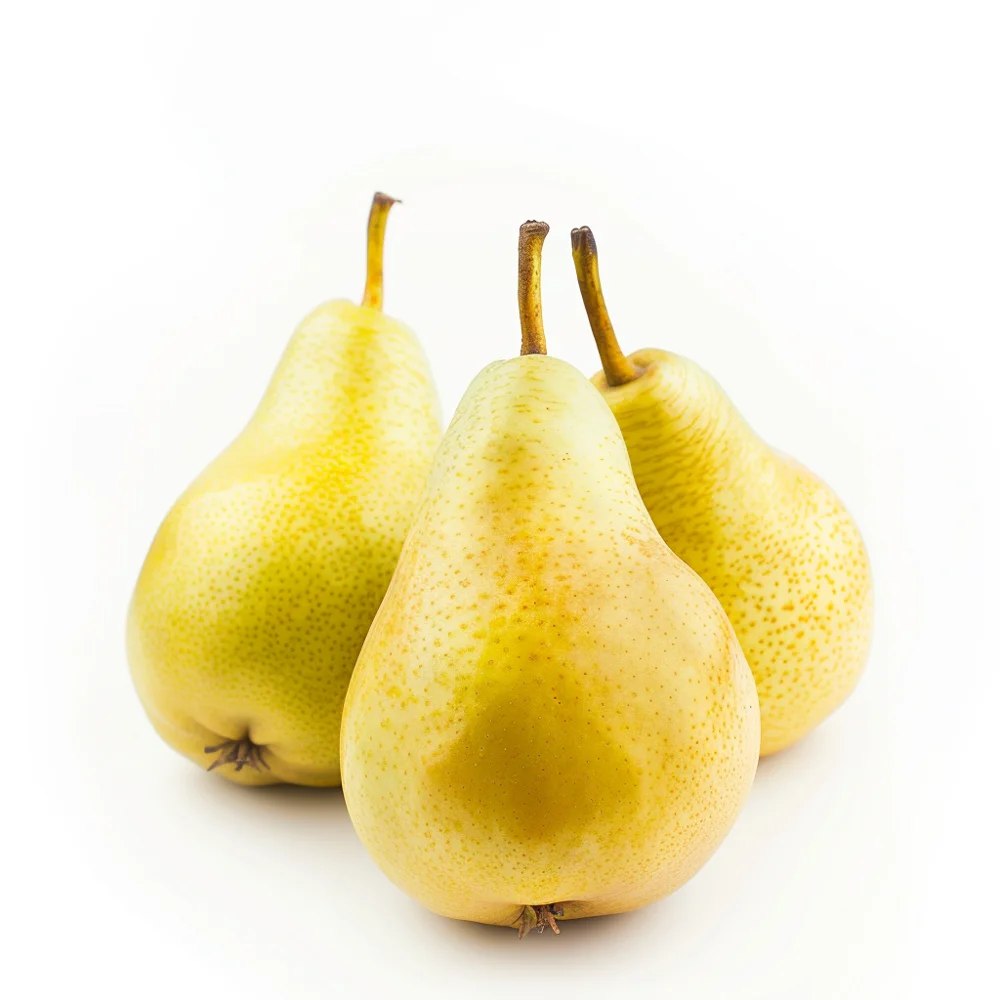
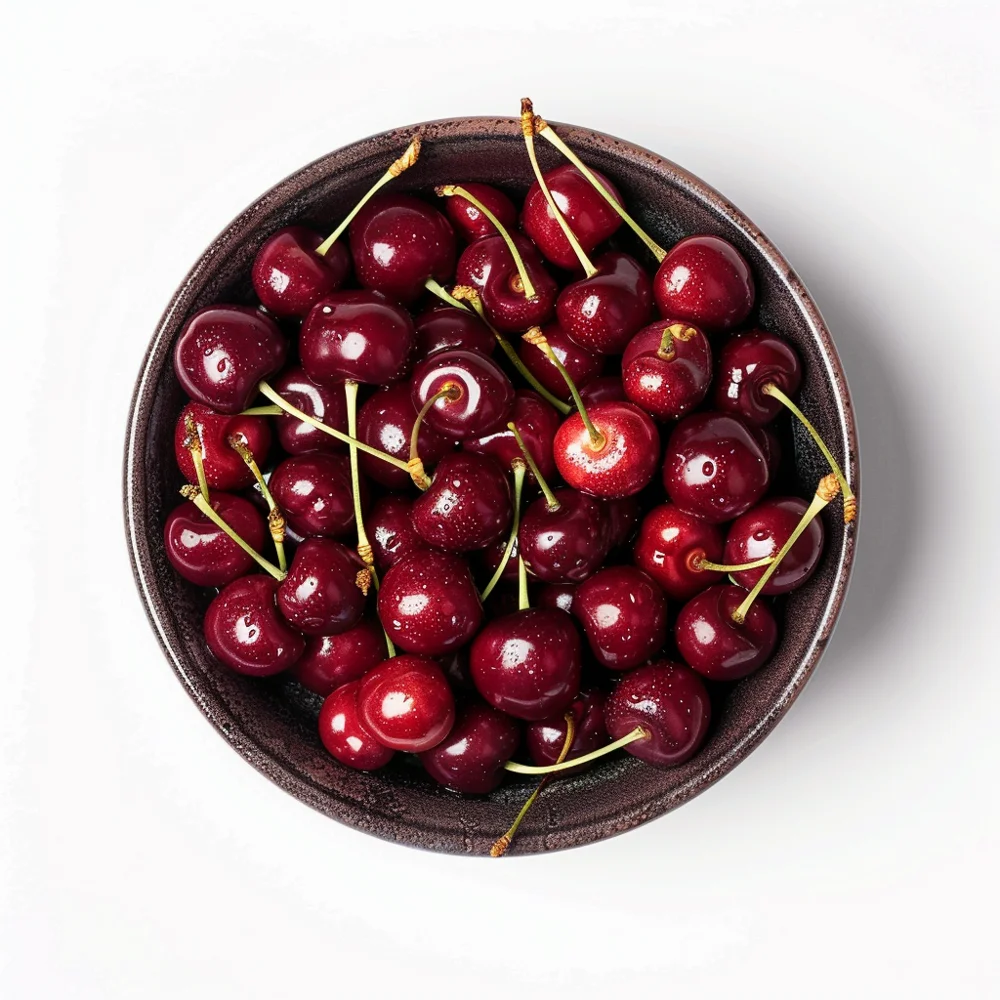




Fruits with a low GI release sugar into the bloodstream more slowly, helping people with diabetes maintain stable blood sugar levels. They can include:
| Fruits | Serving Size | GI Index | GL per serving | Key Nutrients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cherries | 1 cup (120 g) | 20 | 3 | Antioxidants, Fiber, Vitamin C |
| Apricots | 4 apricots (120 g) | 34 | 5 | Vitamin A, Vitamin C |
| Apples | 1 medium-sized fruit (120 g) | 38 | 6 | Fibre, Vitamin C |
| Pears | 1 medium-sized fruit (120 g) | 38 | 4 | Fibre, Vitamin K |
| Oranges | 1 medium-sized fruit (120 g) | 40 | 5 | Vitamin C, Fibre |
| Strawberries | 1 cup (120 g) | 41 | 3 | Vitamin C, Fiber, Antioxidants |
| Blueberries | 1 cup (120 g) | 53 | 9 | Antioxidants, Vitamin C |
Disclaimer: This information is intended for general guidance only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a doctor or dietitian before making any dietary changes, particularly if you have diabetes or other health conditions. Glycemic index values may vary slightly depending on factors such as variety, ripeness, and preparation of the fruit.
Fruits to Avoid: High GI Fruits and Their Impact on Blood Sugar
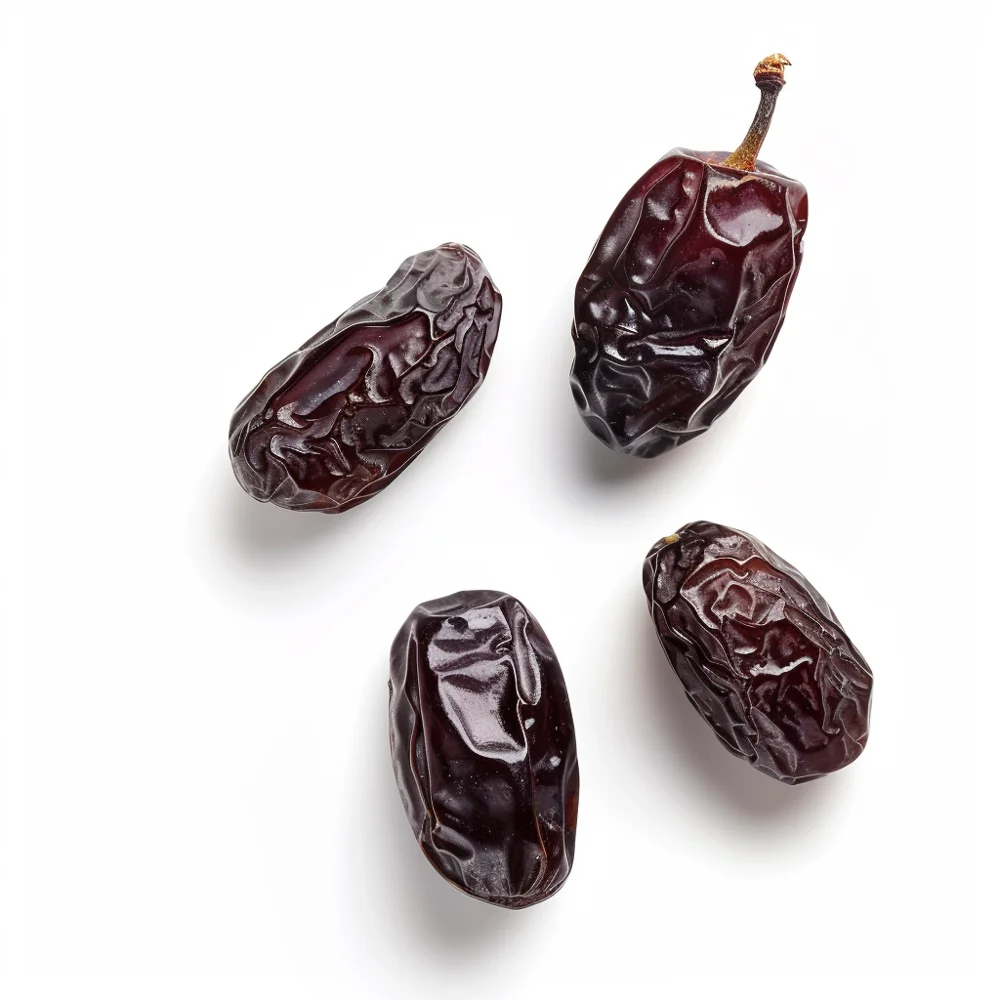




Although high glycemic index (GI) fruits can provide nutritional advantages, people with diabetes should pay attention to the amount they eat and how often they consume them. These fruits include:
| Fruits | Serving Size | GI Index | GL per serving | Key Nutrients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mango | ¾ cup (120 g) | 60 | 8.5 | Vitamin C, Vitamin A, Folate |
| Ripe Bananas | 1 medium-sized fruit (120 g) | 62 | 16 | Potassium, Vitamin B6, Vitamin C |
| Pineapple | Slightly less than 1 cup | 66 | 8 | Vitamin C, Manganese |
| Rockmelon | Slightly less than 1 cup (120 g) | 71 | 4 | Vitamin C, Vitamin A, Potassium |
| Watermelon | Slightly less than 1 cup (120 g) | 72 | 4 | Vitamin C, Vitamin A, Lycopene |
| Dried Dates | 7-8 pieces (60 g) | 103 | 42 | Fibre, Potassium, Magnesium, Antioxidants |
Why Fiber-Rich Fruits Are Important for Diabetes Management
Fibre plays a crucial role in diabetes management as it helps slow the absorption of sugar, leading to more stable blood sugar levels. Fibre-rich fruits like oranges, pears, and kiwis are excellent choices for individuals with diabetes. These fruits not only provide essential nutrients but also contribute to better satiety and digestion, reducing the risk of blood sugar spikes.
Portion Control for Diabetes

In addition to focusing on low-GI fruits, portion control is key for managing blood sugar levels. It's generally recommended to limit fruit intake to one small fruit or about one cup of sliced fruit per serving, such as a small apple or a handful of berries. Spreading fruit consumption throughout the day can help prevent blood sugar spikes. Pairing fruits with high-protein or high-fibre foods, such as nuts or yoghurt, can also slow sugar absorption and support stable blood sugar levels.
Is Fruit Juice a Good Option? Whole Fruit vs. Juice
While fruit juice may seem like a healthy option, it lacks the fibre that whole fruits provide. Fruit juices, especially store-bought varieties, can contain added sugars and lead to rapid increases in blood sugar. Whole fruits, with their fibre content and benefits for blood sugar management, are generally a better option for individuals with diabetes.

Summary: Enjoy Fruits While Managing Diabetes
Fruits are an important part of a balanced diet for individuals with diabetes. Whether it’s a handful of berries or a crisp apple, fruits offer essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health. By choosing fibre-rich, low-GI fruits and keeping portion sizes in check, you can enjoy all the nutritional benefits without worrying about blood sugar spikes. If you are unsure about your choices, it is advisable to consult with a doctor or dietitian for personalised advice tailored to your diabetes management needs.
Why Choose ATA Medical?







Delivering Care Patients Appreciate
What to Expect
FAST RESULTS
We strive to deliver your results within 7 working days.
MINIMUM WAITING TIME
Our patient-oriented processes ensure your waiting time is kept to a minimum.
Friendly Service
Service is a top priority for us at ATA Medical.
Email Us at camden@atamed.sg
for More Information.
Book Your Diabetes Screening With Us at 88750352.

