Fatty Liver Treatment Singapore
Last updated: Feb 12, 2026
What Is Fatty Liver?
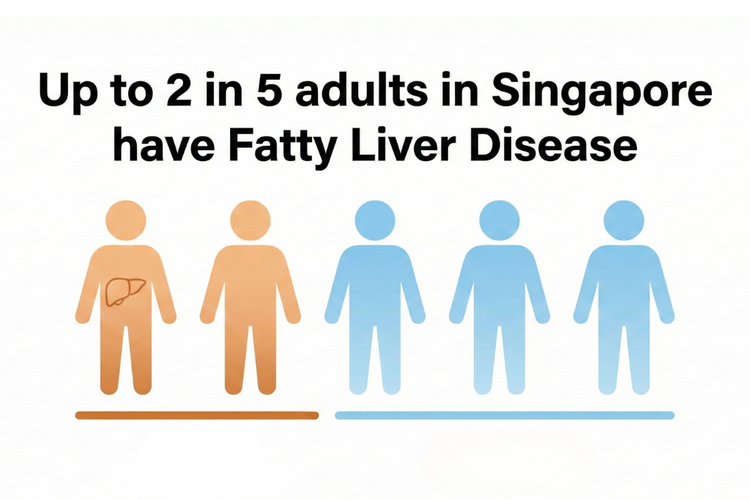
Fatty liver, also known as steatotic liver disease, refers to the abnormal build-up
of fat in liver cells.
It is classified into two main types: metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic
liver disease (MASLD) and alcohol-related liver disease (ALD).
MASLD is more common and is closely associated with metabolic conditions such as obesity,
insulin resistance, type
2 diabetes, high
cholesterol, and high blood pressure.
In Singapore, fatty liver affects up to 40% of adults, largely due
to the increasing prevalence of metabolic and lifestyle-related risk factors. If left
unmanaged, it can progress to liver inflammation (steatohepatitis), scarring (fibrosis),
cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer.
Treatment for fatty liver depends on the severity and underlying cause, and may involve lifestyle changes, management of metabolic conditions, reducing alcohol intake, and in some cases, medication.
What Causes Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver can occur due to a range of lifestyle, metabolic, and genetic factors. The most common causes include:
- Obesity, particularly central (abdominal) fat accumulation
- Insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes
- High blood pressure and elevated cholesterol or triglyceride levels
- Sedentary lifestyle and unhealthy dietary habits
- Excessive alcohol consumption (in the case of ALD)
- Genetic predisposition or family history of liver disease
- Certain medications (e.g. corticosteroids, chemotherapy)
- Medical conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome or hypothyroidism
- Rapid weight loss or malnutrition
- Chronic viral hepatitis (e.g. hepatitis B or C)
What Are the Symptoms of Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver is often silent in its early stages, with most individuals experiencing no symptoms. When signs do appear, they may include:
- Persistent fatigue or low energy
- Discomfort or dull ache in the upper right abdomen
- Mild jaundice in more advanced disease
- Unexplained weight loss
If the condition progresses, complications such as steatohepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis, or liver failure can develop. Fatty liver disease is closely linked to cardiovascular disease, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.

Fatty Liver Grades
Fatty liver can be classified into three grades based on the proportion of liver cells containing fat. These grades help indicate the severity of fat accumulation but do not reflect the extent of liver damage.
| Grade | Description |
|---|---|
| Grade 1 (Mild Fatty Liver) |
|
| Grade 2 (Moderate Fatty Liver) |
|
| Grade 3 (Severe Fatty Liver) |
|
Stages of Fatty Liver Disease
While grading reflects fat accumulation, staging describes how far the disease has progressed in terms of liver damage. These stages are especially important for long-term prognosis.
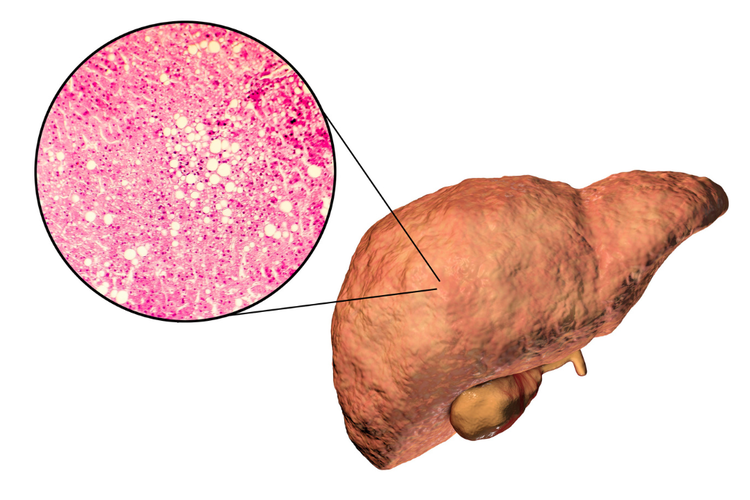
1. Simple Steatosis (Fatty Liver, No Inflammation)
- Fat is present in liver cells but no significant inflammation or damage.
- Usually reversible with lifestyle modifications.
2. Steatohepatitis (Alcoholic or Non-Alcoholic)
- Fat accumulation with inflammation and liver cell damage.
- Increased risk of liver scarring (fibrosis) and disease progression.
- Requires medical management to prevent further damage.
3. Fibrosis (Liver Scarring)
- Ongoing inflammation leads to scar tissue formation, reducing liver function over time.
- Still potentially reversible if the underlying cause is addressed.
4. Cirrhosis (Severe Liver Scarring)
- Extensive and permanent scarring of the liver causing irreversible damage that impairs liver function
- Increases the risk of liver failure and liver cancer
- Can be managed to reduce complications and slow progression
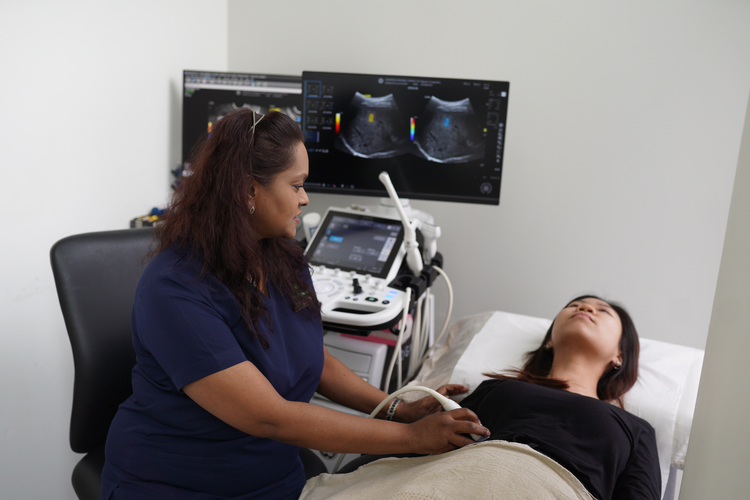
How Is Fatty Liver Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of fatty liver typically involves a combination of clinical assessment, blood
tests, and imaging to confirm fat accumulation and evaluate disease severity.
Common diagnostic tools include:
- Blood tests – Detect liver inflammation or dysfunction by measuring liver enzymes (e.g. alanine aminotransferase [ALT], aspartate aminotransferase [AST]) and other markers in the blood
- Ultrasound scan – Identify fat accumulation by using sound waves to produce images of the liver
- FibroScan® (transient elastography) – Estimate liver stiffness, which may indicate fibrosis, by sending painless vibrations into the liver through a handheld probe
- MRI or CT scans – Assess liver fat content and structural changes through detailed cross-sectional imaging; MRI quantifies fat, while CT provides anatomical detail (size, shape, and texture)
- Liver biopsy – Confirm diagnosis and assess disease severity by extracting a small sample of liver tissue for examination under a microscope
What Are the Treatment Options for Fatty Liver?
Treatment for fatty liver focuses on addressing the underlying metabolic causes and preventing further liver damage. While no single drug cures the condition, several approaches can help improve liver health:
| Treatment | How It Works |
|---|---|
| Weight loss | Weight reduction decreases fat stored in liver cells and reduces liver inflammation. Losing 7–10% of body weight has been shown to significantly improve liver fat levels and may even reverse early-stage fatty liver disease by relieving metabolic stress. |
| Dietary changes | A balanced diet rich in vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins reduces fat accumulation in the liver. Limiting added sugars and saturated fats supports liver repair and overall metabolic health. |
| Regular physical activity | Aerobic and resistance exercises improve insulin sensitivity and reduce liver fat, even without significant weight loss. Physical activity also benefits cardiovascular and metabolic function. |
| Addressing underlying metabolic conditions | Managing metabolic risk factors and related conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol helps slow disease progression and reduces the risk of complications, including cardiovascular disease. |
| Avoiding alcohol | Alcohol avoidance removes a key source of liver stress. This is essential in alcohol-related liver disease (ALD) and may also help prevent worsening of liver function in metabolic-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). |
| Medications | GLP-1 receptor agonists (e.g. semaglutide, tirzepatide), used to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity, have been shown to reduce liver fat and inflammation. These medications may be suitable for patients with metabolic risk factors as part of overall disease management. |
Regular follow-up with your doctor is important to monitor treatment progress, detect complications early, and adjust your management plan if needed.
When Should You See a Doctor?
You should consider consulting a doctor if you:
- Have risk factors such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, a sedentary lifestyle, or a family history of liver disease.
- Experience unexplained fatigue, abdominal discomfort, or abnormal liver blood test results.
- Have a history of excessive alcohol consumption.
- Wish to include liver screening as part of your health check-up.
- Have been diagnosed with fatty liver and require guidance on treatment or monitoring.
- Have chronic hepatitis B or C, which can increase your risk of developing fatty liver disease.
Cost of Fatty Liver Treatment in Singapore
At ATA Medical, we offer liver assessments and personalised treatment strategies to help monitor and manage your liver health. The prices are as follows:
| Treatment | Price*^ |
|---|---|
| Consultation | From $49.05 |
| Blood Tests | |
|
Liver Function
Test A Total Bilirubin, Alkaline Phosphatase [ALP], ALT/SGOT, AST/SGPT, Gamma GT |
$30.52 |
|
Liver Function Test B Total Bilirubin, Alkaline Phosphatase [ALP], ALT/SGOT, AST/SGPT, Gamma GT, Total Protein, Albumin, Globulin, A/G Ratio |
$34.88 |
|
Liver Function Test C Total Bilirubin, Alkaline Phosphatase [ALP], ALT/SGOT, AST/SGPT, Gamma GT, Total Protein, Albumin, Globulin, A/G Ratio, LDH, Hepatitis Bs Antigen & Antibody, Hepatitis A Total IgG, Alpha Fetoprotein [AFP] |
$91.56 |
| Imaging Tests | |
| Ultrasound Liver (Full Hepatobiliary Scan [HBS]) | $196.20 |
| Ultrasound Liver Elastography | $272.50 |
| Ultrasound Liver (HBS) with Elastography | $337.90 |
| MR Liver Elastography | $654 |
| MRI Abdomen (Kidney, Liver, Pancreas, Gallbladder & Spleen) | $1,613.20 |
| Weight Loss Treatments | |
| Oral Appetite Suppressants | From $200 |
| Weight Loss Injections | From $436 / month |
^Prices last updated on Feb 12, 2026. While every effort is made to keep pricing information up to date, please contact our team to confirm the latest rates.
For a more comprehensive review of your health, consider our health screening packages.
As part of our weight loss programme, we provide complimentary InBody body composition analysis during follow-up visits to monitor fat loss, muscle preservation, and overall body composition progress.
Where to Seek Fatty Liver Treatment in Singapore
ATA Medical @ Orchard
Nearest MRT: Orchard Boulevard Station (TE13)
Contact Number: 6223 0682
Email: camden@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed
ATA Medical @ Tanjong Pagar
Nearest MRT: Tanjong Pagar Station (EW15)
Contact Number: 6223 0682
Email: hi@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed
ATA Medical @ Jurong
Nearest MRT: Jurong East MRT Station (NS1/EW24)
Contact Number: 6348 6292
Email: jurong@atamed.sg
Opening Hours:
Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM, 1:30 PM to 5:30 PM
Sat: 8:30 AM to 12:30 PM
Sun & PH: Closed


